Abstract
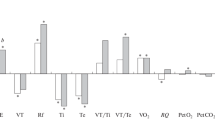
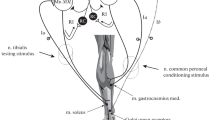
In experiments on frogs tetanus toxin, in doses causing generalized tetanus, depressed reciprocal inhibition of spinal reflexes. The depression of inhibition was not connected with blocking of depolarization of the central endings of primary afferent fibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
A. D. Ado, in: Clinical Problems of Infectious Pathology [in Russian], Moscow (1965), p. 248.
D. M. Gol'dfarb, “The pathogenesis of experimental tetanus poisoning”, Doctoral Dissertation, Moscow (1952).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii, Tetanus [in Russian], Moscow (1966).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii and A. Kh. Kasymov, Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 10, 65 (1964).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii and V. K. Lutsenko, Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 2, 16 (1969).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii and V. K. Lutsenko, Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 4, 33 (1969).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii, and V. K. Lutsenko, Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 8, 25 (1970).
A. A. Polgar, V. S. Smirnova, and G. N. Kryzhanovskii, Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 5, 22 (1972).
A. I. Roitbak, Trudy Inst. Fiziol. im. I. S. Beritashvili,8, 93 (1950).
Yu. S. Sverdlov, Neirofiziologiya,1, 18 (1969).
Yu. S. Sverdlov and V. I. Alekseeva, Fiziol. Zh. SSSR, No. 12, 1442 (1965).
Yu. S. Sverdlov and S. N. Kozhechkin, in: Mechanisms of Nervous Activity [in Russian], Leningrad (1969), p. 136.
J. L. Barker and R. A. Nicoll, Science,176, 1043 (1972).
D. H. Barron and B. H. C. Matthews, J. Physiol. (London)92, 276 (1938).
V. B. Brooks, D. R. Curtis, and J. C. Eccles, J. Physiol. (London),135, 655 (1957).
D. R. Curtis, D. Felix, C. J. A. Game, et al., Brain Res.,51, 358 (1973).
R. A. Davidoff, Science,175, 331 (1972).
J. R. Davies, R. S. Morgan, E. A. Wright, et al., Arch. Int. Physiol.,62, 248 (1954).
R. F. Schmidt, Ergebn. Physiol.,63, 20 (1971).
A. K. Tebecis and J. W. Phillis, Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,28, 1303 (1969).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erzina, G.A., Sverdlov, Y.S. Electronic dorsal-foot potentials of the frog spinal cord in experimental tetanus. Bull Exp Biol Med 80, 740–742 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00809874
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00809874