Summary
Prealbumin plasma level is considered a good index of liver function in liver cirrhosis. However, plasma protein levels depend not only on liver function, but also on amino acid supply which is consequent to nutritional status.
In 12 cirrhotics we measured prealbumin plasma levels and the lower limb venous-artero difference of amino acid plasma levels in blood samples taken from femoral vein and femoral artery in post-absorptive conditions considered as a direct index of protein release from peripheral tissues and an indirect index of protein nutritional status.
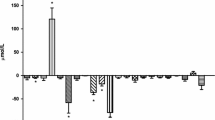
In arterial and in venous plasma amino acid sum was 1.86±0.40 (mean + sd) and 2.00 ± 0.04 mMol/l respectively.
Prealbumin plasma levels were found directly correlated with the venousartero difference of amino acid plasma levels (r = 0.57p < 0.05) and of glutamate + glutamine levels (r = 0.73p < 0.007).
In conclusions, these data suggest that prealbumin plasma levels are linked to amino acid supply from peripheral tissues in cirrhotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers I, Hartmenn H, Bircher J, Creutzfeld W (1989) Scand J Gastroenterol 24: 269–276
Amodio P, Lauro S, Rondana M, Crema G, Merkel C, Gatta A, Ruol A (1991) Respiration 58: 106–111
Bernstein LH, Leukhardt-Fairfield CL, Pleban W, Rudolph R (1989) Clin Chem 35: 271–274
Burnstein AV, Galambos JT (1981) Dig Dis Sci 26: 1078–1083
Coulter JR, Hann CS (1968) J Chromatogr 36: 42–49
Forster J, Greig PD, Glynn MFX, Poon A, Levy G, Superina RA, Langer B (1989) Transplant Proc 21: 2308–2310
Harris CK, Tigane E, Hanes CS (1961) Can J Biochem Physiol 39: 439–451
Hutchinson DR, Smith MG, Parke DV (1981) Clin Chim Acta 114: 69–74
Lehninger AL (1970) Biochemistry. Worth Publishers, New York, p 437
Lindskow J (1982) Acta Med Scand 212: 295–302
Malina RM (1978) Growth of muscle tissue and muscle mass. In: Falkner F, Tanner JM (eds) Human growth, vol. 2. Balliere Tindall, London, pp 273–294
Mancini D, Carbonara AC, Hermans JF (1965) Immunochemistry 2: 235–237
Merkel C, Bolognesi M, Finucci GF, Angeli P, Caregaro L, Rondana M, Gatta A (1989) J Hepatol 9: 16–22
Rondana M, Milani L, Merkel C, Caregaro L, Gatta A (1987) Digestion 37: 72–78
Sachs E, Bernstein LH (1986) Clin Chem 32: 339–341
Shetty PS, Watrasiewicz KE, Jung RT, James WPT (1979) Lancet ii: 230–232
Smith J, Horozitz J, Henderson JM, Heymsfield J (1982) Am J Clin Nutr 35: 56–72
Tyngstrup N, Vilstrup H (1983) Lab Res Meth Biol Med 7: 17–41
Young VR, Steffee WP, Pencharz PB, Winterer JC, Scrimshaw NS (1975) Nature 253: 192–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amodio, P., Bellon, S., Merkel, C. et al. Are prealbumin plasma levels linked to amino acid supply from peripheral tissues in liver cirrhosis?. Amino Acids 3, 223–228 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805996
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805996