Conclusions
A distinguishing feature of the production of the powder material 29NK with specified level of CLTE from powder components is the smaller amount of cobalt contained in the mechanical mixture compared with the amount required for the cast alloy. This has obviously to do with the more intense evaporation of nickel and iron in the process of structure formation occurring under conditions of lengthy vacuum sintering at 1280–1300°C.
The influence of the grain size distribution of the component powders and of the sintering regimes on the CLTE of the powder material 29NK was established. It was noted that reducing the maximal grain size to 50–63 pm and simultaneously extending the sintering time to 20 h ensures the required value of the CLTE; this is due to the complete termination of the process of structure formation and the production of material with the specified chemical and phase composition.
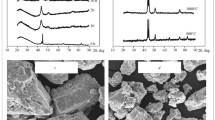
The special features of fracture by impact bending of specimens of the powder material 29NK were examined. It was shown that there is no correlation between the rupture work Ar and the number and area of oxide inclusions; this is connected with pore nucleation in the regions of intense plastic flow, independently of the connection with particles of inclusions. It was established that Ar is affected by structural inhomogeneities connected with the production technology. It was shown that Ar is dependent on the area of the “bands of in-homogeneity” which cause crack nucleation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. K. Borisova (ed.), Precision Alloys with Particular Properties of Thermal Expansion and Elasticity (Handbook) [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1972).
V. Ya. Anosov, Fundamentals of Physicochemical Analysis [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1976).
V. I. Mikheeva, The Method of Physicochemical Analysis in Inorganic Synthesis [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1975).
A. G. Tumanov (ed.), Methods of Testing, Inspecting, and Investigating Engineering Materials (Handbook) [in Russian], Vol. 2, Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1974).
E. A. Shvedkov, Elementary Mathematical Statistics in Experimental Problems of Material Science [in Russian], Naukova: Dumka, Kiev (1975).
N. V. Manukyan, A. E. Sarkisyan, A. B. Safaryan, and G. Kh. Karapetyan, “Cermet ironnickel-cobalt alloys type Kovar, “ Mezhvuzovskii Sbornik Nauchnykh Trudov,3, 99–103 (1980).
H. Scott, American Institute of Mining and Metallurgical Engineers Technical Publication, No. 318, 67 (1930).
I. D. Radomysel'skii, S. G. Napara-Volgina, and V. B. Deimontovich, “The effect of the dispersity of the initial materials on the degree of homogenization of powdered ironchromium alloys,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 9, 1–9 (1971).
J. Fellows (ed.), Fractography and Atlas of Fractograms (Handbook) [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, No. 12(300), pp. 45–52, December, 1987.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kem, A.Y., Zelenskii, V.I. Influence of the chemical composition and of heat-treatment regimes on the properties of the powder material 29NK. Powder Metall Met Ceram 26, 987–994 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797787
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797787