Abstract
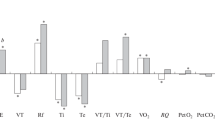
Electrical activity of the thoracic muscles and the oxygen consumption of the animal were studied in unanesthetized cats with pre-implanted electrodes. Heating the cats in a climatic chamber led to a marked increase in the minute volume of respiration, accompanied by a reduction in the oxygen consumption of the animal and a decrease in the combined electrical activity in the serratus, external oblique abdominal, and internal and external intercostal muscles. Activity in the diaphragm and the interchondral muscles was unchanged during hyperpnea. The results point to a decrease in the heat production in the thoracic muscles during thermal hyperpnea as a result of a decrease in the electrical activity of most of the respiratory muscles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
P. N. Veselkin, Thermal Hyperpnea [in Russian], Leningrad (1945).
S. R. Gutman, Electronic Apparatus for Electrophysiological Research [in Russian], Moscow (1969).
A. F. Davydov and Kh. Ul'masov, in: Proceedings of a Conference on Heat Formation and Temperature Regulation of the Body under Normal and Pathological Conditions [in Russian], Kiev (1971).
K. P. Ivanova, The Muscular System and Chemical Thermoregulation [in Russian], Moscow-Leningrad (1965).
C. Albers, Pflüg. Arch. ges. Physiol.,274, 148 (1961).
W. S. Fowler, Am. J. Physiol.,154, 405 (1948).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolupaev, B.I. Activity of the thoracic muscles during thermal hyperpnea. Bull Exp Biol Med 78, 994–995 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00796645
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00796645