Summary
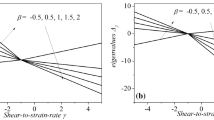
The development of a compressible boundary layer over a wedge impulsively set into motion is studied in this paper. The initial motion is independent of the leading edge effect and the solutions are those of a Rayleigh-type problem. The motion tends to an ultimate steady state of Falkner-Skan type. The equations governing the transient boundary layer from the initial steady state to the terminal steady-state change their character after certain time due to the leading edge effect and thereafter solution depends on both the end conditions. Numerical solutions are obtained through the second-order accuracy upwind scheme. The effects of the Falkner-Skan parameter and the surface temperature on the transient flow and heat transfer are also studied. It has been found that the flow separation does not occur form≧−0.0707 when θ w = 1.5 (hot wall), andm≧−0.118 when θ 0.5 (cold wall).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewartson, K.: On the impulsive motion of a flat plate in a viscous fluid. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 4 (1951) 182–192
Schlichting, H.: Boundary layer theory. New York: McGraw-Hill 1968
Dennis, S. C. R.: The motion of a viscous fluid past an impulsively started semi-infinite flat plate. J. Ins. Math. Appl. 10 (1972) 105–117
Hall, M. G.: The boundary layer over an impulsively started flat plate. Proc. Roy. Soc. London A. 316 (1969) 401–414
Wang, J. C. T. On the numerical methods for the singular parabolic equations in fluid dynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 52 (1983) 464–479
Wang, J. C. T. Renewed studies on the unsteady boundary layers governed by singular parabolic equations. J. Fluid Mech. 52 (1985) 413–427
Van de Vooren, A. I.;Botta, E. F. E.;Stout, J.: The boundary layer on a disk at rest in a rotating fluid. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 40 (1987) 15–32
Smith, S. H. The impulsive motion of a wedge in a viscous fluid. ZAMP 18 (1967) 508–522
Nanbu, K.: Unsteady Falkner-Skan flow. ZAMP 22 (1971) 1167–1172
Williams, J. C.;Rhyne, T. B.: Boundary layer development on a wedge impulsively set into motion. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 38 (1980) 215–224
Varga, R. S. Matrix iterative analysis. New York: Prentice-Hall 1962
Williams III, J. C.;Johnson, W. D. Semisimilar solutions to unsteady boundary flows including separation. AIAA J. 12 (1974) 1388–1393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, S., Gupta, A.S. Transient compressible boundary layer on a wedge impulsively set into motion. Arch. Appl. Mech. 66, 336–342 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795250
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795250