Conclusions
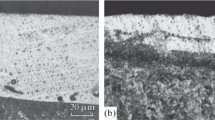
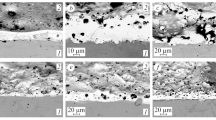
A study was made of electric-spark alloying with alumina-containing titanium nitride composites sintered in argon and nitrogen. It was established that the most vavorable conditions of formation of a reinforced layer obtain in alloying with a TiN + 30 vol. % Al2O3 material sintered in argon. In alloying with TiN-Al2O3 composites, the conditions of formation of a reinforced layer deteriorate greatly when anodes sintered in nitrogen, rather than in argon, are used. In the ESA of steel with TiN-Al2O3 materials their erosion is less than that of the ZrN- Al2O3 composites investigated earlier, because the extent of brittle fracture accompanying the treatment is reduced. The erosion of TiN-Al2O3 materials is much less than that of pure TiN, as a result of which the coefficient of gransfer in ESA with TiN-Al2O3 anodes is four times higher. In view of this, alumina may be recommended as an effective addition to TiN-base electrode materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
L. M. Kirilyuk, “Investigation of the process of titanium nitride coating formation by deposition from a gaseous phase on dense P/M materials,” Author's Abstract of Candidate's Dissertation, Minsk (1979).
C. Leśniak, “Sintered carbides coated with WC and TiN,” Metal. Proszków,8, No. 1, 16–21 (1975).
V. T. Bondar', “Investigation of the conditions of formation of nitride coatings on a hard-metal surface,” Author's Abstract of Candidate's Dissertation, Kiev (1977).
A. D. Verkhoturov, F. F. Egorov, and V. T. Bondar', “Electric-spark alloying of steel with heterophase materials based on ZrN and Al2O3,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 4, 51–56 (1980).
G. V. Samsonov, Nitrides [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1969).
G. V. Samsonov, A. D. Verkhoturov, G. V. Bovkun, and V. S. Sychev, Electric-Spark Alloying of Metallic Surfaces [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1976).
B. D. Storozh, “Investigation of the processes of formation of cermets based on some refractory metals,” Author's Abstract of Candidate's Dissertation, Kiev (1975).
F. F. Egorov and P. S. Kislyi, “Reactions of zirconium nitride with alumina and molybdenum,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 6, 43–47 (1978).
F. F. Egorov and E. S. Lugovskaya, “Effect of nitrogen on the sintering of ZrN-Al2O3 mixtures,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 10, 11–14 (1977).
A. D. Verkhoturov, F. F. Egorov, and V. T. Bondar', “Electric-spark alloying of steel with heterogeneous molybdenum-containing zirconium nitride materials,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 6, 57–61 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, No. 12(240), pp. 50–54, December, 1982.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egorov, F.F., Verkhoturov, A.D., Poveshchenko, V.I. et al. Electric-spark alloying of steel with heterophase materials based on TiN and Al2O3 . Powder Metall Met Ceram 21, 947–951 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00794336
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00794336