Conclusions
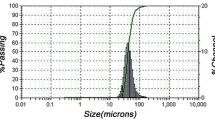
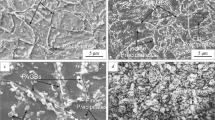
The density, volume shrinkage, chemical composition, structure, and mechanical properties of P/M Kh25 steel are determined by the conditions under which it is sintered and by the nature of the sintering atmosphere employed. The ductility of the steel is higher after sintering in a vacuum compared with sintering in dissociated ammonia, because these two environments have different effects on the chemical composition and structure of the steel. Use of cold and hot forging enables high-density P/M Kh25 steel to be obtained which is comparable to solid steels in most properties and actually superior to them in impact toughness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. A. Dovydenkov and I. D. Radomysel'skii, “Effect of sintering technology on the structure and properties of 20Kh13 martensitic-ferritic chromium steel,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 8, 81–85 (1981).
F. F. Khimushin, Stainless Steels [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1967).
I. M. Fedorchenko, I. G. Slys', and L. A. Sosnovskii, “Technology of sintering of powder metallurgical materials without a circulating protective atmosphere,” Poroshk, Metall., No. 5, 26–32 (1972).
S. S. Kiparisov and G. A. Libenson, Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1960).
I. V. Kudryavtsev (ed.), Materials in Machine Construction (Handbook) [in Russian], Vol. 3, Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1968).
J. Bark and P. Weiss, Powder Metallurgy of Materials for Special Applications [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1977).
H. A. Kuhn and C. L. Downey, “Effect of metal flow and fracture on the design of blanks for powder forging,” Powder Metall. Powder. Technol.,10, No. 1, 59–65 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
25% Cr stainless steel. 15Kh25T and Kh28, which are referred to elsewhere in this article, are 0.15% C-25% Cr-Ti and 28% Cr grades, respectively — Translator.
Translated from Poroshkovay Metallurgiya, No. 12(240), pp. 35–39, December, 1982.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nel'zina, I.V., Radomysel'skii, I.D. Production and properties of P/M Kh25 steel. Powder Metall Met Ceram 21, 935–938 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00794332
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00794332