Conclusions
-
1.
A study was made of the effect of hot-pressing parameters on some properties of PZhlM iron powder layers sinter-bonded to Type 45 steel substrate.
-
2.
The variation of the density and properties of sinter-bonded layers with hot-pressing temperature, pressure, and time is similar to that characterizing the hot pressing of iron powder compacts, although the actual values of density obtained are slightly higher because of the small thickness of such powder layers.
-
3.
The optimum conditions have been established by experiment for the application of an iron powder layer to a steel substrate by the hot-pressing process.
-
4.
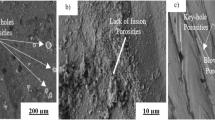
Metallographie examinations have shown that dense, defect-free layers are formed under conditions ensuring high values of bond strength (32 kgf/mm2). Under these conditions the surface layers of the substrates experience decarburization, whose intensity depends on the process temperature and time, and the layers themselves exhibit recrystallization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
N. F. Kazakov and L. N. Lado, “Vacuum diffusion welding of sintered materials to lowcarbon steel,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 10, 100–104 (1969).
V. N. Miroshnikov et al., “Vacuum diffusion sinter bonding of iron-base powder metallurgical components to steel,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 9, 18–24 (1972).
N. V. Avdeev, “Fundamental principles of metal spray deposition,” Sb. Tr. Mekh. Fak. Tashkentsk. Politekh. Inst., Tashkent, No. 102, 99–101 (1973).
V. A. Martynov, V. P. Petrenko, et al., “A vibratory hot-pressing stand,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 9, 97–100 (1976).
R. G. Berezin, V. A. Martynov, et al., “Methods of determining the strength of adhesion of spray-deposited metal layers to their substrates,” Zavod. Lab., No. 2, 226–228 (1974).
R. G. Berezin, V. A. Martynov, et al., “Determination of the strength of adhesion of spray-deposited metal layers to their substrates,” Zavod. Lab., No. 10, 1266–1268 (1974).
G. V. Samsonov and M. S. Koval'chenko, Hot Pressing [in Russian], Gostekhizdat Ukr. SSR, Kiev (1962).
M. Yu. Bal'shin, Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Mashgiz, Moscow (1948).
N. F. Vyaznikov and S. S. Ermakov, Powder Metallurgy Materials and Parts [in Russian], Mashgiz, Leningrad (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, No. 3(183), pp. 37–43, 1978.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynov, V.A., Koval'chenko, M.S., Berezin, R.G. et al. Structure and properties of sinter-bonded iron powder layers produced by hot pressing. Powder Metall Met Ceram 17, 197–202 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00791428
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00791428