Summary
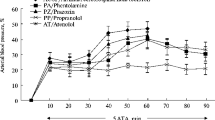
Studies were made of the oxygen saturation in arterial blood in animals during exposure to 7500 m in a chamber. The study was carried out after the photoelectrical method by means of continous oxyhemometry in rabbits and cats with denervation of carotid sinus zones, as well as in controls. In the controls the saturation diminished, to 55–62% and increased somewhat after 8–10 minutes' exposition to “altitude”. In the experimental animals the diminution of oxygen saturation was more pronounced, reaching 40–50% and remained within this range during the whole period of exposure.
The experiments demonstrated that the dynamics and the degree of oxygen saturation of arterial blood in case of hypoxia depend on the function of the carotid sinus zones.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
E. M. Kreps, M. S. Shipalov, E. A. Bolotinsky, Byull. Eksptl. Biol. i Med., 32, No. 7, 60–64 1951.
W. C. Grant, Am. Journ. of Physiol., 1951, v. 164 No. 1, pp. 226–233.
M. Terzioglu E. Goral, J. J., Bradav, Am. of Physiol., 1955, v. 182, No. 1, p. 100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beller, N.N. The role of interoceptors in the regulation of oxygen saturation of arterial blood. Bull Exp Biol Med 43, 654–659 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00784320
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00784320