Summary
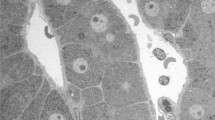
Using electron microscopy, we investigated how cellular debris, formed in the Disse space during cholestasis, was cleared. Ten patients with cholestasis of varied origin and severity were studied and compared with 10 controls without liver disease. In cholestatic patients, sinusoidal cells contained variable amounts of amylase PAS-positive material. In clean perfusion-fixed sinusoids the endothelial cells often appeared swollen and active, with few fenestrations. Hepatocyte blebs and cellular debris were sometimes seen in the Disse space. Two mechanisms were apparently involved in the clearing process: phagocytosis by macrophages either infiltrated into the Disse space, or forming the barrier; and the passage of debris from the Disse space into the sinusoidal lumen through the endothelial wall. Debris was either forced through enlarged pores or through the wall, with a progressive invagination followed by an outpouching in the lumen. The force, possibly provided by endothelial massage, may not be sufficient to push out cellular debris from the Disse space; morphological data seemed to indicate that endothelial damage may be a necessary factor. Debris present in the lumen was phagocytized by numerous active macrophages. Cellular debris was not observed in the Disse space of control patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankston PW, Pino RM (1980) The development of the sinusoids of foetal liver: morphology of endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, and the transmural migration of blood cells into sinusoids. Am J Anat 159:1–15
Bardadin KA, Desmet VJ (1985) Ultrastructural observations on sinusoidal endothelial cells in chronic active hepatitis. Histopathology 9:171–181
Bardadin KA, Scheuer PJ (1984) Endothelial cell changes in acute hepatitis. A light and electron microscopic study. J of Pathol 144:213–220
De Broe ME, Wieme RJ, Logghe GN, Roels F (1977) Spontaneous shedding of plasma membrane fragments by human cells in vivo and in vitro. Clin Chim Acta 81:237–245
Desmet VJ (1972) Morphologic and histochemical aspects of cholestasis. In: Popper H, Schaffner F (eds) Progress in Liver Diseases, Vol IV. Grune and Stratton, New-York, p 97–132
Desmet VJ, De Vos R (1983) Structural analysis of acute liver injury. In: Keppler D, Popper H, Bianchi L, Reutter W (eds) Mechanisms of hepatocyte injury and death. MTP Press, Lancaster, p 11–30
Gendrault JL, Montecino-Rodriguez F, Cinqualbre J (1982) Structure of the normal human liver sinusoid after perfusion fixation. In: Knook DL, Wisse E (eds). Sinusoidal liver cells. Elsevier Biomedical, Amsterdam, p 93–100
Grimaud JA, Borojevic R (1977) Chronic human schistosomiasis Mansoni. Pathology of the Disse's space. Lab Invest 36:268–273
Jones EA, Summerfield JA (1985) Functional aspects of hepatic sinusoidal cells. Semin in Liver Dis 5:157–174
Phillips J, Oda M, Funatsu K (1979) Reactions of the liver to injury. In: Farber E, Fisher MM (eds). Toxic injury of the liver. Part A. Marcel Dekker Inc, New-York, p 333–383
Phillips MJ, Fisher RL, Anderson DW, Lan SP, Lachin JM, Boyer JL (1983) Ultrastructural evidence in intrahepatic cholestasis before and after chenodeoxycholic acid therapy in patients with cholelithiasis: the National cooperative Gallstone study. Hepatology 3:209–220
Steffan AM, Gendrault JL, Kirn A (1986) Phagocytosis and surface modulation of fenestrated areas - two properties of murine endothelial liver cells (E) involving microfilaments. In: Kirn A, Knook DL, Wisse E (eds). Cells of the hepatic sinusoid I. Kupffer Cell Foundation, Rijswijk, p 483–488
Steiner JW, Carruthers JS, Kalifat SR (1962) Vascular alterations in the liver of rats with extrahepatic biliary obstruction. An electron and fluorescent microscopic study. Exp Mol Pathol 1:427–456
Sztark F, Dubroca J, Latry P, Quinton A, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P (1986a) Perisinusoidal cells in patients with normal liver histology: a morphometric study. J of Hepatol 3:358–369
Sztark F, Latry P, Quinton A, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P (1986b) The sinusoidal barrier in alcoholic patients without liver fibrosis: a morphometric study. Virchows Archiv 409:385–393
Wisse E, De Zanger R, Jacobs R (1982) Lobular gradients in endothelial fenestrae and sinusoidal diameter favour centrolobular exchange processes: a scanning EM study. In: Knook DL, Wisse E (eds). Sinusoidal liver cells. Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, p 61–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the CNRS (RCP 724)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubuisson, L., Bioulac-Sage, P., Boussarie, L. et al. Removal of cellular debris formed in the Disse space in patients with cholestasis. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 410, 501–507 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00781685
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00781685