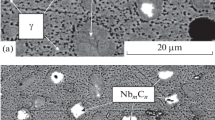
Conclusions
The character of phase transformations in different heats of alloy ÉP539 with compositions within the limits specified differs considerably. Larger amounts of aluminum and titanium with constant amounts of other alloying elements may lead to formation of as much as 10% tcp phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
F. F. Khimushin, Heat-Resistant Steels and Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1969).
E. E. Levin et al., "Structure and properties of heat-resistant alloy ÉP539, intended for gas turbine vanes," Tr. TsKTI im I. I. Polzunova, No. 105, 3 (1971).
N. F. Lashko (editor), Physicochemical Methods of Phase Analysis of Steels and Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1970), p. 278.
H. Beattie and W. Hagel, Trans. AIME,233, No. 2, 277 (1965).
Additional information
I. I. Polzunov Central Scientific-Research and Design-Planning Institute of Boilers and Turbines. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 22–25, May, 1979.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pigrova, G.D. Phase composition of heat-resistant alloy ÉP539. Met Sci Heat Treat 21, 353–356 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00780772
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00780772