Conclusions
-
1.
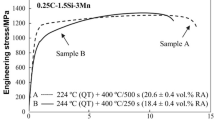
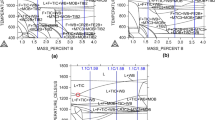
A high cooling rate of bronze castings leads to a structure of refined α phase and a substantial quantity of β phase (α+ℋ), which reduces the ductile characteristics of the alloy.
-
2.
By controlling the cooling rate and the concentrations of the components it is possible to obtain the optimal combination of strength and ductile characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 12, pp. 42–44, December, 1980.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prokhorov, I.I., Shebatinov, M.P. & Polushkin, N.A. Effect of the composition and crystallization conditions on the properties and type of fracture of AZhN bronze. Met Sci Heat Treat 22, 902–904 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779404
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779404