Summary
The response of barley to phosphate application and the effect of applied phosphorus on the uptake of soil zinc by the crop were tested in pot, Neubauer and incubaticn experiments on four soils differing in native phosphate status.
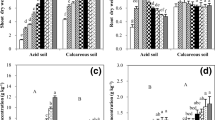
There was a response of the yield to phosphorus application in alluvial soils from Clementina (Ecuador) and Bangla Desh. Barley grown on red soil from Bangla Desh and glacial clay from Uppsala did not show any response to P application.
Applied P32 was fixed to a great extent in all the soils studied. But in phosphate-deficient soils, a much higher degree of sorption of P32 was recorded than in phosphate-rich soils. Compared to phosphate-rich soils, the utilization of fertilizer phosphorus is higher than of native soil P in the case of phosphate-deficient soils. It was observed that uptake of Zn65 by the crop is counteracted by phosphorus application at the three stages of crop growth studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boawn L. C., Viets F. G.Jr., and Crawford C. L., Effect of phosphate fertilizers on zinc nutrition of field beans. Soil Sci.78, 1–7 (1954).
Burlson C. A., Dacus A. D., and Gerrard C. J., The effect of phosphorus fertilization on the zinc nutrition of several irrigated crops. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.25, 365–368 (1961).
Chapman H. D., The diagnosis and control of zinc deficiency and excess. Bull. Res. Coun. Israel8D, 105–130 (1960).
Egnér H., Riehm H., and Domingo W. R., Untersuchungen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung des Nährstoffzustandes des Böden. 2. Chemische Extraktionsmethoden zur Phosphor- und Kaliumbestimmung. Kgl. Lantbr. högsk. Ann.26, 199–215 (1960).
Johansson A., Cobalt — an expedient agent in soil testing for T, S and exchange-able Ca, Mg and Mn. Soil Sci.91, 364–368 (1961).
Kanwar J. S., Dhingra D. R., and Randhawa N. S., Chemical composition of healthy and chlorotic leaves of citrus plants in the Punjab. Indian J. Agr. Sci.33, 268–271 (1963).
Laker M. C., Uptake of zinc and phosphorus by plants from a sandy soil. South African J. Agr. Sci.10, 323–330 (1967).
Morril, L. G., M. S. Thesis, Utah State Agr. College, Logan, Utah (1956).
Ozanne P. G., Shaw T. C., and Kirlon D. J., Pasture response to traces of zinc in phosphate fertilizers. Australian J. Exp. agric. Animal Husb.5, 29–33 (1965).
Stukenholtz D. D., Olsen R. J., Gogan G. et al., On the mechanism of phosphorus zinc interaction in corn nutrition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.30, 759–763 (1966).
Viets F. G.Jr., Boawn L. C., and Crawford C. L., Zinc content of bean plants in relation to deficiency symptoms and yield. Plant Physiol.29, 76–79 (1954).
Ward R. C., Langin E. J., Olson R. A. et al., Factors responsible for poor response of corn and grain sorghum to phosphorus fertilization. III. Effect of soil compaction, moisture levels and other properties on P-Zn relations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.26, 326–330 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was financially supported by the International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria, and by the National Council for Forestry and Agricultural Research, Sweden.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motsara, M.R. On the effects of phosphorus on zinc uptake by barley. Plant Soil 38, 381–392 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779020
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779020