Summary
Methods for labelling growing plants by exposing them to C14O2 under a cellulose acetate-butyrate canopy have been developed for laboratory and field use. The length of labelling ranged from 2 to 33 days and the C14O2 content of the atmosphere was automatically controlled. This made it possible to measure carbon assimilation by the plants, transfer of photosynthates beneath ground and respiration of the roots.
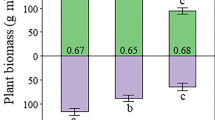
In the laboratory, root respiration of wheat plants was measured by separating the above and beneath ground plant parts using a RTV rubber partition. Half to two thirds of the assimilated carbon was found above ground, 15 to 25 per cent in the roots and shoot bases below the partition and 17 to 25 per cent was lost by underground respiration. The variability of these proportions was related to the stage of maturity of the plants.
On native grassland, the relative above and beneath ground productivity was 50 per cent. The time required for the photosynthates to reach the roots at various depths ranged from 1 to 5 days and the amount of material deposited in the roots changed with time and soil moisture content. The use of tubes inserted at various depths beneath the canopy permitted sampling of soil air for C14 and CO2 measurements. The soil C14O2 flux indicated that root respiration during 8 days accounted for 24 per cent of the labelled carbon translocated to the roots after a two days labelling period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coupland R. T. and Johnson R. E., Rooting characteristics of native grassland species in Saskatchewan. J. Ecol.53, 475–507 (1965).
Dahlman R. C. and Kucera C. L., Tagging native grassland vegetation with carbon-14. Ecology49, 1199–1203 (1968).
Halm, B. J., Stewart, J. W. B., and Halstead, R. L., The phosphorus cycle in a native grassland ecosystem, paper IAEA/SM-151/7.In: Symposium on the use of isotopes and radiation in research on soil-plant relationships, Vienna, Dec. 1971.
Jenkinson D. S., Studies on the decomposition of C14 labelled organic matter in soil. Soil Sci.111, 64–70 (1971).
Jong, E. de, and Schappert, H. J. V., Calculation of soil respiration and activity from CO2 profiles in the soil. Soil Sci. (in press).
Kriedemann P. E., C14 distribution in lemon plants. J. Hort. Sci.44, 273–279 (1969).
Nelson C. D., Effect of climate on the distribution and translocation of assimilates.In: Environmental Control of Plant Growth. L. T. Evans (ed.) pp. 149–174. Academic Press, Inc., New York (1963).
Shamoot S., McDonald L. and Bartholomew W. V., Rhizodeposition of organic debris in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.32, 817–820 (1968).
Sorenson L. H. and Paul E. A., Transformation of acetate carbon into carbohydrates and amino acid metabolites during decomposition in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem.3, 173–180 (1971).
Stotzky G., Culbreth W., and Gish L. B., A sealing compound for use in biological work. Nature191, 410 (1961).
Turner J. C., Triton X-100 scintillant for carbon-14 labelled materials. Intern. J. Applied Radiat. Isotopes19, 557–563 (1968).
Warembourg, F. R., Studies of carbon transfer rates within the plant soil system.In: Isotope Methodology and Techniques in Soil-plant Nutrition and Plant Physiology. Rennie, D. A. and Paul, E. A. (ed.) Saskatchwan Inst. Pedol. No.76, pp. 81–91 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Warembourg, F.R., Paul, E.A. The use of C14O2 canopy techniques for measuring carbon transfer through the plant-soil system. Plant Soil 38, 331–345 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779017
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779017