Conclusions
-
1.
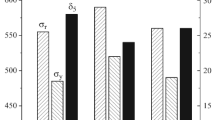
Cold bending of tubular blanks of 10Kh2M steel has an insignificant influence on the level of microdistortions, decreases the lattice parameter somewhat, does not change the phase composition of the carbides, and leads to cracking of the coarse M23C6 carbides.
-
2.
Tempering at 710°C after bending reduces the level of microdistortions by more than three times and the intrinsic broadening of the (110) line by more than two times, increases the lattice parameter, and changes the phase composition of the carbide phase (M3C dissolves).
-
3.
The stress-rupture strength of 10Kh2M steel coils in the unheat treated condition is higher at stresses exceeding 160 N/mm2 than in the heat treated condition, which is the result of the favorable kinetics of occurrence of structural transformations. With stresses below 160 N/mm2 and in service for 105 h at 505°C coils in the heat treated condition, that is, with a more stable structure, possess higher stress-rupture strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. S. Gorelik, X-Ray Diffraction and Electron Diffraction Analysis [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1970).
A. N. Ivanov, "Determination of broadening of the x-ray line from Fourier coefficients", Zavod. Lab., No. 4, 57–58 (1981).
D. M. Kheiker and L. S. Zevin, X-Ray Diffractometry [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1963).
A. G. Vasil'eva, Deformation Strengthening of Hardened Constructional Steels [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1981).
Koreaki Tamaki and Jippei Suzuki, "Precipitation of carbides during tempering of Cr-Mo steels", Res. Repts. Fac. Eng. Mic. Unire, No. 7, 39–52 (1982).
Zh. P. Pastukhova, A. G. Rakhshtadt, and Yu. A. Kaplun, Dynamic Aging of Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1985).
D. Stephen, "On the toughness increment associated with the austenite to martensite phase transformation in TRIP steels", Met. Trans.,2, No. 8, 2135 (1971).
I. N. Bogachev, L. S. Malinov, and T. D. Éismondt, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Met., No. 5, 168 (1971).
P. A. Antikain, Metals and Calculation of the Strength of Boilers and Piping [in Russian], Énergiya, Moscow (1980), p. 69.
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 53–56, August, 1988.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antikain, P.A., Lepekhina, L.I., Borisov, V.E. et al. Influence of heat treatment on the structure and stress-rupture strength of 10Kh2M steel tubing. Met Sci Heat Treat 30, 627–630 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00778271
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00778271