Conclusions
-
1.
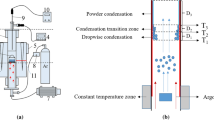
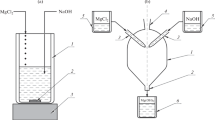
With increasing precipitation time, the particle size of the powder decreases in accordance with a linear law, but the particle coarsening is not proportional to the weight gain of specimens.
-
2.
The dependence of powder particle size on vapor concentration in the starting mixture over the evaporation-temperature range investigated also obeys a linear relationship.
-
3.
With rise in condensation temperature, the powder becomes finer in accordance with an exponential law.
-
4.
The presence of an oxidizing agent in the gas does not lead to powder comminution with rise in condensation temperature.
-
5.
The particle size of the metal being precipitated varies depending on the nature of the inert gas: it is smaller in argon than in helium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. S. Mikulinskii, I. V. Frishberg, and G. I. Belyaeva, Poroshkovaya Met., No. 5 (1963).
I. V. Frishberg, Tr. Inst. Met., No. 11 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, No. 7 (67), pp. 12–18, July, 1968.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frishberg, I.V., Mikulinskii, A.S. Dependence of powder particle size on condensation conditions, determined on the example of metallic magnesium. Powder Metall Met Ceram 7, 517–522 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00774696
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00774696