Abstract
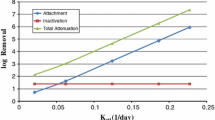
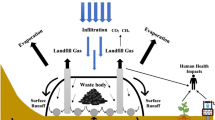
This report summarizes research studies linking on-site waste disposal systems (OSDS) to pathogen and nutrient concentrations in groundwater with the potential to impact coastal embayments. Few studies connect OSDS to coastal water quality. Most studies examined pathogen and nutrient impacts to groundwater and omitted estimations of contaminants discharged to surface water. The majority of studies focused on nitrogen, with little information on pathogens and even less on phosphorus. Nitrogen discharged from OSDS poses the greatest threat to water quality. Vertical distance of septic tank infiltration system from the water table, septic system design, and siting remain the key components in minimizing potential impacts from OSDS for control of both pathogens and nutrients. The most comprehensive information connecting nutrient contributions from OSDS to surface water quality was the study conducted on Buttermilk Bay in Massachusetts where 74% of nitrogen to the bay was attributed to onsite disposal systems. In conclusion, further studies on the viability and transport of pathogens and nutrients through the groundwater aquifer and across the groundwater/surface-water interface are needed. Additional research on the importance of septic system design on the availability of contaminants to groundwater as well as the minimum distance between the septic system and water table necessary to protect groundwater are also indicated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DL, Lewis AL, and Sherman KM (1990) Onsite sewage disposal research project in florida. Human enterovirus monitoring at onsite sewage disposal systems in florida. Ayres Associates, Florida Department of Health and Rehabilitative Service under contract no. LCND2 Florida Department of HRS, Tallahassee. 10 pp
Carlile BL, Cogger CG, Sobsey MD, Scandura J, and Steinbeck SJ (1981) Movement and fate of septic tank effluent in soils of the North Carolina Coastal Plain. Department of Soil Sciences, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina. 100 pp
Craun GF (1979) Waterborne disease outbreaks in the United States. J Environ Health 41:259–265
Hagerdorn C, Hansen DT, and Simonson GH (1978) Survival and movement of fecal indicator bacteria in soil under conditions of saturated flow. J Environ Qual 7:55–59
Horsley Witten Hegeman, Inc. (1991) Quantification and control of nitrogen inputs to Buttermilk Bay, Vol I. Barnstable, Massachusetts. 32 pp
Hurst CJ, Benton WH, and McClellan KA (1988) Thermal and water source effects upon the stability of enteroviruses in surface freshwaters. Can J Microbiol 35:474–480
Inland Bays Task Force (1984) Protecting Delaware's inland bays: Charting a course for change. Wilmington News Journal. 4 July 1984
MacIntyre WG, Johnson GH, Reay WG, and Simons GM (1989) Ground water nonpoint sources of nutrients to the southern Chesapeake Bay. Proceedings of ground water issues and solutions in the Potomac River Basin/Chesapeake Bay region conference. 14–16 March 1989. George Washington University, Washington, DC. 21 pp
Melnick JL and Gerba CP (1980) Viruses in water and soil. Public Health Rev 9(3–4): 28 pp
Miller JC (1972) Nitrate contamination of the water table in Delaware. Delaware Geological Survey Report of Investigations no. 20., Newark, Delaware
Pancorbo OC, Evansheen BG, Campbell WF, Lambert S, Curtis SK, and Wooley TW (1987) Infectivity and antigenicity reduction rates of human rotavirus strain Wa in freshwaters. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1803–1811
Reneau RB Jr (1977) Changes in organic nitrogenous compounds from septic tank effluent in a soil with fluctuating water table. J Environ Qual 6:173–178
Reneau RB Jr (1979) Changes in concentrations of selected chemical pollutants in wet, tile drained soil systems as influenced by disposal of septic tank effluents. J Environ Qual 8:189–196
Reneau RB Jr and Pettry DE (1975) Movement of coliform bacteria from septic tank effluent through selected coastal plain soils of Virginia. Environ Qual 4:41–44
Ritter WF (1986) Nutrient budgets for the inland bays. Technical report. Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control, Dover, Delaware. 70 pp
Ritter WF (1990) Impact of alternative onsite wastewater system on ground water quality in delaware. Agricultural Engineering Department, University of Delaware, Newark. 114 pp
US EPA (1983a) Rural lakes project handbook. Region 5, Water Division, Chicago. 41 pp
US EPA (1983b) Final environmental impact statement: wastewater management in rural lake areas. Region 5, Water Division, Chicago, 287 pp
US EPA (1990) Annual progress report for the baywide nutrient strategy, Chesapeake Bay Program, Annapolis, Maryland. 3 pp
Yates MV (1985) Septic tank density and groundwater contamination. Groundwater 23(5): 5 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, P.J. Water quality impacts from on-site waste disposal systems to coastal areas through groundwater discharge. Geo 26, 262–268 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00770477
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00770477