Abstract
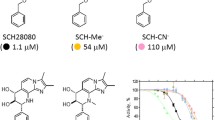
The gastric H,K-ATPase is an alpha,beta heterodimer. The large catalytic subunit is composed, in the case of the hog enzyme, of 1033 amino acids, whereas the beta subunit is composed of about 291 amino acids and is heavily glycosylated. The membrane topology of the alpha subunit is difficult to predict using hydropathy analysis. Tryptic hydrolysis of intact, inside out vesicles followed by cysteine labelling with fluorescein-5-maleimide provided experimental evidence for an 8 membrane spanning model for the alpha subunit, between residues 104 and 162 (M1/M2), 291 and 358 (M3/M4), 776 and 835 (M5/M6), and 853 and 946 (M7/M8). No evidence was found for a pair of segments (M9/M10) towards the C terminal end of the molecule, contrary to predictions for the Na,K- and Ca-ATPases. Iodination of intact vesicles followed by carboxypeptidase Y cleavage of the C terminal tyrosines showed that the C terminal end of the alpha subunit was cytoplasmic. The epitope for antibody 146 was extracytoplasmic and located between residues 871 to 874 between M7/M8. The binding site of the K competitive imidazo-pyridine, SCH28080, was to the extracytoplasmic loop between M1 and M2, whereas the binding of the covalent SH reagent generated from acid activation of omeprazole in acid transporting vesicles was to 2 cysteines at positions 813 (or 822) and 892 predicted to be in the extracytoplasmic loops connecting M5/M6 and M7/M8, respectively. The beta subunit was only hydrolysed in broken vesicles. A fragment beginning at position 236 was liberated under these conditions only in the presence of reducing agents, showing that cysteine 210 and 263 were disulfide linked. It seems that this subunit has only a single membrane spanning segment as predicted by hydrophobicity. Binding of either SCH28080 or omeprazole to the extracytoplasmic face of the enzyme affected cytoplasmic conformational changes, showing that there was transmembranal transmission of changes of shape of the protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamberg, K., Mercier, F., Reuben, M. A., Kobayashi, I., Munson, K. B., and Sachs, G. (1992).Biochim. Biophys. Acta, in press.
Besancon, M., Mercier, F., Shin, J. M., Munson, K., Miller, M., Hersey, S. J., and Sachs, G. (1992).J. Biol. Chem., submitted.
Capasso, J. M., Hoving, S., Tal, D. M., Golshleger, R., and Karlish, S. J. D. (1992).J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1150–1158.
Clarke, D. M., Loo, T. W., and Maclennan, D. H. (1990a).J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6262–6267.
Clarke, D. M., Loo, T. W., and Maclennan, D. H. (1990b).J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17405–17408.
Geering, K. (1990).J. Membr. Biol. 115, 109–121.
Hall, K., Perez, G., Anderson, D., Gutierrez, C., Munson, K., Hersey, S. J., and Sachs, G. (1990).Biochemistry 29, 701–706.
Homreda, H., Kawakami, K., Nagano, K., and Matsui, H. (1989).Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 5742–5745.
Horisberger, J. D., Jaunin, P., Reuben, M. A., Lasater, L. S., Chow, D. C., Forte, J. G., Sachs, G., Rossier, B. C., and Geering, K. (1991).J. Biol. Chem. 266, 19131–19134.
Kirley, T. L. (1989).J. Biol. Chem. 264, 7185–7192.
Linberg, P., Nordberg, A., Brandstrom, A., and Wallmark, B. (1986).J. Med. Chem. 29, 1327–1329.
Lorentzon, P., Jackson, R., Wallmark, B., and Sachs, G. (1987).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 897, 41–51.
Matthews, I., Sharma, R. P., Lee, A. G., and East, J. M. (1990).J. Biol. Chem. 265, 18737–18740.
Mercier, F., Reggio, H., Devilliers, G., Bataille, D., and Mangeat, P. (1989).J. Cell Biol. 108, 441–453.
Munson, K. B., Gutierrez, C., Balaji, V. N., Ramnayaran, K., and Sachs, G. (1991).J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18976–18988.
Price, C. E., and Lingrel, J. B. (1988).Biochemistry 27, 8401–8410.
Rabon, E., Hall, K., Perez, G., and Sachs, G. (1991a).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1077, 173–179.
Rabon, E., Sachs, G., Bassilian, S., Leach, C., and Keeling, D. (1991b).J. Biol. Chem. 266, 12395–12340.
Rabon, E., Bassilian, S., Sachs, G., and Karlish, S. J. D. (1991c).J. Biol. Chem. 19594–19599.
Reuben, M. E., Lasater, L. S., and Sachs, G. (1990).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6767–6771.
Scott, D., Munson, K., Modyanov, N., and Sachs, G. (1991).FASEB J. 5, A478.
Shull, G. E., and Lungrel, J. B. (1986).J. Biol. Chem. 261, 16788–16791.
Tai, M., Im, W. B., Davis, J., Blakeman, D., Zurcher-Neely, H., and Heinrikson, R. (1989).Biochemistry 28, 3183–3187.
Tamura, S., Tagaya, M., Maeda, M., and Futai, M. (1989).J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8580–8584.
Walderhaug, M. O., Post, R. L., Saccomani, G., Leonard, R. T., and Briskin, D. P. (1985).J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3852–3859.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sachs, G., Besancon, M., Shin, J.M. et al. Structural aspects of the gastric H,K-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24, 301–308 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768850
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768850