Abstract
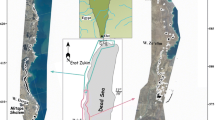
The central Ebro Basin comprises thick evaporite materials whose high solubility produces typically karstic landforms. The sinkhole morphology developed in the overlying alluvium has been studied using gravimetry and ground-penetrating radar (GPR) on stream terraces, as well as analyzing the evolution of sinkhole morphologies observed in aerial photographs taken in 1928, 1957, and 1985. The sinkhole morphologies give some idea of possible subsurface processes as well as an indication of the final mechanisms involve in sinkhole development. On stream terraces and cover pediments the most commonly encountered dolines are bowl-shaped in their morphology with both diffuse and scarped edges. In contrast, dolines developed in the gypsiferous silt infilled valleys have a funnel and well-shaped morphology. The diffuse-edged bowl-shaped dolines are developed through the progressive subsidence of the alluvial cover, due to washing down of alluvial particles through small voids and cracks into deeper subsurface caves, resulting in a decrease alluvial density. Future compaction of the alluvial cover will produce surface subsidences. This type of dolines are associated with negative gravity anomalies. In contrast, the scarped-edge dolines are formed by the sudden collapse of a cavity roof. The cavities and cracks formed in the gypsum karst may migrate to the surface through the alluvial deposits by piping, and they may subsequently collapse. In this instance, the cavities can be detected by both gravity and GPR anomalies where the voids are not deeper than 4–5 m from the surface. These processes forming sinkholes can be enhanced by man-induced changes in the groundwater hydrologic regime by both inflows, due to irrigation, ditch losses, or pipe leakages, and by outflows from pumping activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen AS (1969) Geologic settings of subsidence. In: Varnes DJ and Kiersch G (Eds.), Geological Society of America Reviews in Engineering Geology 2:305–342
Beck BF (Ed.) (1989) Engineering and environmental impacts of sinkholes and karst. Proceedings of the third multidisciplinary conference on sinkholes and the environmental impacts of karst, Orlando, Florida. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema 384 pp
Beck BF and Wilson WL (Eds.) (1987) Karst Hydrogeology: Engineering and environmental applications. Proceedings of the second multidisciplinary conference on sinkholes and the environmental impacts of karst, Orlando, Florida. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema 467 pp
Benito G (1987) Karstificación y colapsos kársticos en los yesos del sector central de la Depresión del Ebro. Cuatern Geomorfol 1:61–76
Benito G and Casas AM (1987) Small-scale deformations in Quaternary deposits in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. Geol Mediterran 15(4): 233–243
Benito G and Gutiérrez M (1988) Karts in gypsum and its environmental impact on the middle Ebro Basin, Spain. Environ Geol Water Sci 12(2):107–111
Benito G and Férez del Campo P (1991) Sinkhole evolution in alluvial deposits within the Central Ebro Basin, Northeast Spain. In: Johnson AI (Ed.), Land Subsidence. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, Publ. No. 200:323–331
Benito G and Pérez-González A (1990) Modelo de respuesta compleja de las terrazas del río Gállego en el tramo Zuera-Zaragoza. I Reunión Nacional en Geomorfología. Teruel pp 407–416
Cooper AH (1986) Subsidence and foundering of strata caused by the dissolution of Permian gypsum in the Ripon and Bedale areas, North Yorkshire. In: Harwood GM and Smith DB (Eds.), The English Zechstein and related topics. Geological Society Special Publication 22:127–139
Cvijic J (1893) Das karstphänomen. Geogr. Abhand, von A. Penk, 5(3):215–319
Daoxian Y (1987) Keynote adress: Environmental and engineering problems of karst geology in China. In: Beck BF and Wilson WL (Eds.), Karst Hydrology: Engineering and Environmental Applications. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema pp 1–11
Ege JR (1984) Mechanisms of surface subsidence resulting from solution extraction of salt. In: Holzer TL (Ed.), Man-Induced Land Subsidence. Geological Society of America. Reviews in Engineering Geology 6:203–221
Gutiérrez M, Ibañez MJ; Peña JL; Rodríguez J, and Soriano A (1985) Quelques exemples de karst sur gypse dans la Depresion de l'Ebre. Karstologia 6:29–36
Hue F (1962) Medio siglo de experiencia de un canal en terreno yesoso. I Coloquio Internacional sobre las Obras Públicas en terrenos yesosos. Tema 2, Tomo II pp 103–124
James AN and Lupton ARR (1978) Gypsum and anhydrite in foundations of hydraulic structures. Geotechnique, 28:249–272
Johnson AI (1991) Land subsidence. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, Publ. No. 200:690 pp
Mandado J (1987) Litofacies yesíferas del sector aragonés de la Cuenca Terciaria del Ebro. Petrogénesis y geoquímica. Unpublished doctoral thesis. University of Zaragoza 442 pp
Newton HG and Tanner JM (1987) Case histories of induced sinkholes in the eastern United States. In: Beck BF and Wilson WL (Eds.), Karst Hydrology: Engineering and Environmental Applications. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema pp 15–23
Nicod S (1976) Karst in gypses et des évaporites associées. Ann Geogr 471:513–554
Férez del Campo P (1989) Nuevos datos sobre los colapsos kársticos en la Depresión del Ebro. Deteccióan e incidencia en la nueva línea de alta velocidad Madrid-Barcelona. El Cuaternario de España y Portugal, 2. Madrid: ITGE pp 905–911
Ponsjack E (1940) Deposition of calcium sulfate from sea water. Am J Sci 238:559–568
Rahn PH (1986) Land subsidence. In: Engineering Geology. An Environmental Approach. Amsterdam: Elsevier pp 303–332
Riba O and Llamas MR (1962) Canales de La Violada, Monegros y Flumen. Libro-Guía del Viaje de Estudio núm. 5. I Coloquio Internacional sobre las Obras Públicas en terrenos yesosos. Serv. Geol. de Obras Públicas 23 pp
Sahuquillo A, López-Camacho B, and De Toledo F (1976) Estudio hidrageológico de las terrazas de los ríos Ebro y Gállego en la zona de influencia de Zaragoza. MOPU-Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro 118 pp
Smith DL and Smith GL (1987) Use of vertical gravity gradient analyses to detect near-surface dissolution voids in karst terranes. In: Beck BF and Wilson WL (Eds.), Karst Hydrology: Engineering and Environmental Applications. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema pp 205–210
Soriano A (1986) Dolinas de disolución normal y dolinas aluviales en el sector centro-meridional de la Depresión del Ebro. Bol Geol Min 97:328–337
Soriano MA (1988) Dolinas aluviales y su impacto ambiental en las proximidades de Zaragoza. Congreso Geológico de España 1988. Comunicaciones 2:495–498
Stefanko R (1973) Roof and ground control-subsidence and ground movement. In: Cummis AB and Given IA (Eds.), SAME Mining Engineering Handbook. Society of Mining Engineers of American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers 2, sec. 13 pp 2–9
Sweeting MM (1966) The weathering of limestones, with particular reference to Carboniferous Limestone of northern England. In: Dury GH (Ed.), Essays in Geomorphology. London: Heinemann pp 177–210
Waltham AC (1989) Ground Subsidence. London: Blackie & Son
White EL, Aron G, and White WB (1986) The influence of Urbanization on sinkhole development in central Pennsylvania. Environ Geol Water Sci 8(1–2):91–97
Zuidam RA van (1976) Geomorphological development of the Zaragoza, region, Spanish Int. Institute for Aerial Survey and Earth Sciences (I.T.C.), 211 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benito, G., del Campo, P.P., Gutiérrez-Elorza, M. et al. Natural and human-induced sinkholes in gypsum terrain and associated environmental problems in NE Spain. Geo 25, 156–164 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768545
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768545