Abstract
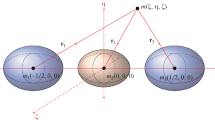
A new approach to the two-body problem is introduced which entails the perturbation of an initially static configuration. It is demonstrated that Einstein's theory demands that the bodies move when the equilibrium-sustaining stress is weakened. Radiation from the system, both during the stress-breaking and free-fall period are discussed. For free-fall, the non-linearities could greatly alter the energy loss rate from that predicted by the ‘quadrupole formula’.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnor, W.B. (1963).Brit. J. Appl. Phys.,14, 555.
Curzon, H.E.J. (1924).Proc. Lond. Math. Soc.,23, 477; for a review of the static two-body problem, see: Darmois, G. (1927).Mém. Sci. Math., Fasc. XXV.
Bach, R. and Weyl, H. (1922).Math. Zeit.,13, 134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by National Research Council of Canada Grants A5340, TO624.
Work performed at the Laboratoire de Physique Théorique, Institut Henri Poincaré under the auspices of the Canada-France Scientific Exchange Visitor Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooperstock, F.I. The axially-symmetric two-body problem. Gen Relat Gravit 6, 91–97 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766607
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766607