Abstract
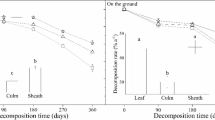
Degradation ofAvicennia marina (Forsk) Vierh. leaf litter was studied in the laboratory for three months. The leaves were incubated in filtered estuarine water in erlenmeyer flasks for various number of days and the amounts of N, P, and K+ remaining in the leaves determined. Weight loss was rapid within the first 24 hours (19%), but slowed down thereafter reaching 30% after six weeks. While P and K+ decreased with time, N decreased initially, then increased rapidly after six weeks. Leaching and microbial activities could be responsible for the nutrient changes. The increase in N may indicate that mangrove leaf litter provides the surface for microbial N synthesis and acts as a reservoir for N.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber, J D. & J. M. Melillo, 1980. Litter decomposition: Measuring state of decay and percent transfer into forest soils. Can. J. Bot. 54: 416–421.
APHA, 1980. Standard Methods for the examination of Water and Wastewater, 15th edition. American Public Health Assoc., Washington, DC. 1134 pp.
Banyikwa, F. F & A. K. Semesi, 1986. Endangered mangrove ecosystems — The case of the Kunduchi and Mbweni mangrove forests. In Mainoya J. R. & P. R. Siegel (eds); Status and Utilization of mangroves. Proc. Workshop on ‚Save the mangrove ecosystem in Tanzania.’ Dar es Salaam: 103–132.
Brinson, M., 1977. Decomposition and nutrient exchange of litter in an alluvial swamp forest. Ecology 58: 601–609.
Bunn, S. E., 1989. Processing of leaf litter in a northern jarrah forest stream, Western Australia: 1. Seasonal differences. Hydrobiologia 162: 201–210.
Chauvet, E., 1987. Changes in the chemical composition of alder, poplar and willow leaves during decomposition in a river. Hydrobiologia 148: 35–44.
Crawford, P. J. & D. M. Rosenberg, 1984: Breakdown of conifer needle debris in a new Northern Reservoir, Southern Indian Lake, Manitoba. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 41: 649–658.
Douce, G. K. & D. A. Crossley, 1982. The effect of soil fauna on litter mass loss and nutrient loss dynamics in arctic tundra at Barrow, Alaska. Ecology 63: 523–532.
Fogel, R. & K. Cromack, 1977. Effect of habitat and substrate quality on Dougal Fir litter decomposition in Western Oregon. Can. J. Bot. 55: 1632–1640.
Golterman, H. L., R. S. Clymo & M. A. M. Ohnstad, 1978. Methods for physical and chemical analysis of freshwaters, 2nd edition. Blackwell Sci. Publ., Oxford: 213 pp.
Imbert, H. B. & J. Pozo, 1989. Breakdown of four leaf litter species and associated fauna in a Basque Country forested stream. Hydrobiologia 182: 1–14.
Killingbeck, K. T., D. L. Smith & G. R. Marsolf, 1982. Chemical changes in tree leaves during decomposition in a tallgrass prairie stream. Ecology 63: 585–589.
Lugo, A. E. & S. C. Snedaker, 1975. The ecology of mangroves. Annu. Rev. Ecol. syst. 5: 39–64.
McCusker, A., 1971. Ecological studies of an area of mangrove vegetation in Tanzania. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Dar es Salaam. (Unpublished).
McCusker, A., 1975. The Kunduchi mangrove basin. Univ. Sci. J. (Dar Univ.) 1: 30–40.
Melillo, J. M., J. A. Aber & J. F. Muratore, 1982. Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63: 621–626.
Melillo, J. M., R. J. Naiman, J. D. Aber & K. N. Eshleman, 1983. The influence of substrate quality and stream size on wood decomposition dynamics. Oecologia 58: 281–285.
Merrill, W. & E. B. Cowling, 1966. Role of nitrogen in wood deterioration: amounts and distribution of nitrogen in tree stems. Can J. Bot. 44: 1555–1580.
Meyer, J. L., 1980. Dynamics of phosphorus and organic matter during leaf decomposition in a forest stream. Oikos 34: 44–53.
Odum, W. E. & E. J. Heald, 1975. Mangrove forests and aquatic productivity. In Hasler, A. D. (ed); Coupling of land and water systems. Springer-Verlag, New York: 129–136.
Odum, E. W., P. W. Kirk & J. C. Zieman, 1979. Non-protein nitrogen compounds associated with particles of vascular plant detritus. Oikos 32: 363–367.
Robertson, A. I., 1988. Decomposition of mangrove leaf litter in tropical Australia. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 116: 235–247.
Steinke, T. D., G. Naidoo & L. M. Charles, 1983. Degradation of mangrove leaf litter and stem tissues in situ in Megeni estuary, South Africa. In Teas, H. J. (ed.); Tasks for vegetation science, vol. 8. Dr W. Junk Publ., The Hague: 141–149.
Suberkropp, K. & M. J. Klug, 1976. Fungi and bacteria associated with leaves during processing in a woodland stream. Ecology 57: 707–719.
Suberkropp, K., G. L. Godshalk & M. J. Klug, 1976. Changes in the chemical composition of leaves during processing in a woodland stream. Ecology 57: 720–727.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chale, F.M.M. Degradation of mangrove leaf litter under aerobic conditions. Hydrobiologia 257, 177–183 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765010
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765010