Abstract
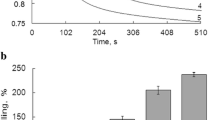
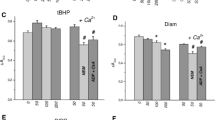
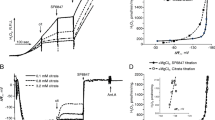
The effect of the alcohol-deterrent drug, disulfiram, on mitochondrial Ca2+ content was studied. Addition of this drug (20 µM) to mitochondria induces a complete loss of accumulated Ca2+. The calcium release is accompanied by a collapse of the transmembrane potential, mitochondrial swelling, and a diminution of the NAD(P)H/NAD(P) radio. These effects of disulfiram depend on Ca2+ accumulation; thus, ruthenium red reestablished the membrane δψ and prevents the oxidation of pyridine nucleotides. The binding of disulfiram to the membrane sulfhydryls appeared to depend on the metabolic state of mitochondria, as well as on the mitochondrial configuration. In addition, it is shown that modification of 9 nmol -SH groups per mg protein suffices to induce the release of accumulated Ca2+.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerman, K. E., and Wikström, M. F. K. (1976).FEBS Lett. 68, 191–197.
Beatrice, M. C., Palmer, J. W., and Pfeifrer, D. F. (1980).J. Biol. Chem. 255, 8663–8671.
Bellomo, G., Jewell, S. A., and Orrenius, S. (1982).J. Biol. Chem. 257, 11,558–11,562.
Bellomo, G., Martino, A., Richelmi, P., Moore, G. A., Jewell, S. A., and Orrenius, S. (1984).Eur. J. Biochem. 140, 1–6.
Brierley, G. P., Knight, V. A., and Settlemire, C. T. (1968).J. Biol. Chem. 243, 5035–5043.
Chávez, E., and Holguín, J. A. (1988).J. Biol. Chem. 263, 3582–3587.
Chávez, E., and Jay, D. (1987).J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 19, 571–580.
Chávez, E., Briones, R., Michel, B., Bravo, C., and Jay, D. (1985).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 242, 493–497.
Chávez, E., Jay, D., and Bravo, C. (1987).J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 19, 285–295.
Ellman, G. L. (1959).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 22, 70–77.
Fossa, A. A., White, J. F., and Carlson, G. P. (1982).Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 66, 109–117.
Graham, W. D. (1951).J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 3, 160–164.
Harris, E. J. (1979).Biochem. J. 178, 673–680.
Hunter, D. F., and Haworth, R. A. (1974).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 195, 453–459.
Jurkowitz, M. S., and Brierley, G. P. (1984).J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 14, 435–449.
Jurkowitz, M. S., Geibuhler, T., Jung, D. W., and Brierley, G. P. (1983).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 223, 120–128.
Keiner, M. J., and Alexander, N. M. (1986).J. Biol. Chem. 261, 1636–1641.
Kendrick, N. C. (1976).Ann. Biochem. 76, 487–501.
Klingenberg, M. (1984). InThe Enzymes of Biological Membranes (Martonosi, A. N., ed.), Vol. 4, Plenum, London/New York, pp. 511–533.
Lehninger, A. L., Vercesi, A. E., and Babanunmi, E. (1978).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 1690–1694.
Lötscher, H. R., Wintherhalter, K. H., Carafoli, E., and Richter, C. (1980).J. Biol. Chem. 255, 9325–9330.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. (1951).J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Nicholls, D. G., and Crompton, M. (1980).FEBS Lett. 111, 261–268.
Palmer, J. W., and Pfeiffer, D. R. (1981).J. Biol. Chem. 256, 6742–6750.
Pfeiffer, D. R., Schmid, P. C., Beatrice, M. C., and Schmid, H. H. O. (1979).J. Biol. Chem. 254, 11,485–11,494.
Ramachandran, C., and Bygrace, F. L. (1978).Biochem. J. 174, 613–620.
Serio, R., Long, R. A., Taylor, J. E., Tolamn, R. L., Weppelman, R. M., and Solson, G. (1984).Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 72, 333–342.
Stoner, C. D., and Sirak, H. D. (1973).J. Cell Biol. 56, 51–64.
Stripp, B., Green, F. E., and Gillete, J. R. (1969).J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 170, 347–354.
Toninello, A., Siliprandi, D., and Siliprandi, N. (1983).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 111, 792–797.
Valenzuela, F., and Vasalle, M. (1983).Cardiovasc. Res. 17, 608–619.
Valenzuela, F., and Vasalle, M. (1985).J. Electrocardiol. 18, 21–34.
Vercesi, A. E. (1984).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 119, 305–310.
Vercesi, A. E. (1987).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 252, 171–178.
Zoccarato, F., Rugolo, M., Siliprandi, D., and Siliprandi, N. (1981).Eur. J. Biochem. 114, 195–199.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chávez, E., Zazueta, C. & Bravo, C. Extensive Ca2+ release from energized mitochondria induced by disulfiram. J Bioenerg Biomembr 21, 335–345 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762725
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762725