Abstract
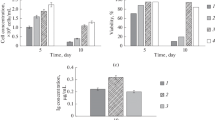
The relationship between growth and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production in the recombinant cell line CHO 320 was studied by varying the foetal calf serum (FCS) concentration. The specific growth rate varied with the initial FCS concentration in a manner which could be well fitted by the Monod model. TheK s and μ max values were found to be 0.771% (v/v) serum and 0.031 h−1 respectively. The average specific IFN-γ production rates during the exponential phase increased with increasing FCS concentration. A good correlation between specific production rate and specific growth rate was found in all phases of the culture except the lag phase and it was clearly demonstrated that IFN-γ production was growth associated. Specific glucose and glutamine utilisation rates were inversely related to specific growth rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Rubeai M, Emery AN, Chalder S, Jan DC (1992) Specific monoclonal antibody productivity and the cell cycle- comparisons of batch, continuous and perfusion cultures. Cytotechnology 9: 85–97.
Buntemeyer H, Wallerius C, Lehmann J (1992) Optimal medium use for continuous high density perfusion processes. Cytotechnology 9: 59–67.
Dalili M and Ollis DF (1989). Transient kinetics of hybridoma growth and monoclonal antobody production in serum-limited cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 33: 984–990.
Fawcett JK, and Scott JE (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea J. Clin. Path. 13: 156–159.
Field RP, Brand H, Renner GL, Robertson HA, Boraston R (1991) Production of a chimeric antibody for tumour imaging and therapy from chinese hamster overy (CHO) and myeloma cells. In: Production of biologicals from animal cells in culture. (Eds.) Spier RE, Griffiths JB, Meignier B, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford pp. 742–744.
Geaugey V, Duval D, Geahel I, Marc A, Engasser JM (1989) Infulence of amino acids on hybridoma cell viability and antibody secretion. Cytotechnology 2: 119–129.
Hayter PM, Curling EMA, Baines AJ, Jenkins N, Salmon I, Strange PG, Bull AT (1991) Chinese hamster ovary cell growth and interferon production kinetics in stirred batch culture. Appl. Microbiol. 34: 559–564.
Hayter PM, Curling EMA, Baines AJ, Jenkins N, Salmon I, Strange PG, Tong JM, Bull AT (1992) Glucose-limited chemostat culture of chinese hamster overy cells producing recombinant human interferon-γ. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 29: 327–335.
Hayter PM, Curling EMA, Gould ML, Baines AJ, Jenkins N, Salmon I, Strange PG, Bull AT (1993) The effect of the dilution rate on the CHO cell physiology and recombinant interferon-γ production in glucose-limited chemostat culture. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 42: 1077–1085.
Hild HM, Emery AN, and Al-Rubeai M, (1992) The effect of pH, temperature, serum concentration and media composition on the growth of insect cells In: Workshop on baculovirus and recombinant protein production processes. Edited by JM Vlak, EJ, Schlaeger and AR, Bernard, March 29–April 1, Interlaken, Switzerland.
Jan DC, Al-Rubeai M, Emery AN (1991) Towards low-cost mediumn formulation for intensive animal cell culture. In: (eds.) Huyghebaert A, and Vandamme E, Upstream and downstream processing in biotechnology III (pp. 1.17–1.26) Royal Flemish Society of Engineers, Antwerpen.
Leelavatcharamas V, (1994) Growth, cell cycle and interferon-γ production of CHO cells in batch culture M. Phil. thesis. School of chemical engineering. University of Birmingham.
Luan YT, Mutharasan R and Magee WE, (1987) Strategies to extend longevity of hybridomas in culture and promote yield of monoclonal antibodies Biotechn. Lett., 9: 691–696.
Reid S, Saxena V, Greenfield PF, Weiss SA (1992) Applicability of fed batch processes for improving recombinant protein production by the baculovirus expression system. In: Spier RE, Griffiths JB, and MacDonald C, Animal cell Technology: developments, processes and products (eds.) pp. 276–281. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford.
Thomas JN, (1990) Mammalian cell physiology in: (eds.) Lubiniecki AS, p 119, Large-scale mammalian cell culture technology, Marcel Dekker Inc. New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leelavatcharamas, V., Emery, A.N. & Al-Rubeai, M. Growth and interferon-γ production in batch culture of CHO cells. Cytotechnology 15, 65–71 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762380
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762380