Abstract
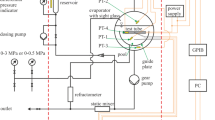
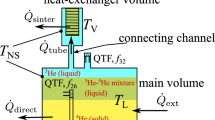
The ballistic regime of liquid3He-4He mixtures is characterized by a large mean free path λ of the thermal excitations compared to the characteristic dimension of the experiment. We report on investigations of the transport properties of mixtures as well as superfluid3He in the ballistic regime by means of the vibrating wire technique. In order to avoid possible sources of heat leaks into the liquid, the experimental setup was built as far as possible of pure materials only. The contribution of a Ag sinter to the heat leak as well as its influence on the attainable minimum temperature of the mixtures were investigated by performing measurements in two similar setups which differed in the size of the heat exchanger by about one order of magnitude. Moreover, we have used the vibrating wire partly immersed in the superfluid3He-B phase of a phase-separated mixture as a very sensitive, continuously monitoring thermometer for liquid mixtures in their ballistic regime. The achieved minimum temperature of a 6.8%-mixture atp = 0.35 bar and of a 9.5%-mixture atp = 9.8 bar was 130 μK. This value can be considered as an upper limit for the temperature of the mixtures as the damping of the vibrating wire thermometer saturates at this temperature due to its intrinsic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. König and F. Pobell, see preceeding paper in this issue, andPhys. Rev. Lett. 71, 2761 (1993).
A review of the results of the Lancaster group is: A. M. Guénault and G. R. Pickett, inHelium Three, W. P. Halperin, L. P. Pitaevskii (eds.), (Elsevier Science Publishers, 1990).
R. M. Mueller, H. Chocholacs, C. Buchal, M. Kubota, J. R. Owers-Bradley, and F. Pobell,Proc. Symp. on Quantum Fluids and Solids, E. D. Adams, G. G. Ihas (eds.); Sanibel Island, USA (1983); H. Ishimoto, H. Fukuyama, N. Nishida, Y. Miura, Y. Takano, T. Fukuda, T. Tazaki, and S. Ogawa,J. Low. Temp. Phys. 77, 133 (1989); G. Oh, M. Nakagawa, H. Akimoto, O. Ishikawa, T. Hata, and T. Kodama,Physica B 165 & 166, 527 (1990).
G.-H. Oh, Y. Ishimoto, T. Kawae, M. Nakagawa, O. Ishikawa, T. Hata, and T. Kodama,Physica B 194–196, 855 (1994),J. Low Temp. Phys. 95, 525 (1994).
R. König, P. Esquinazi, and F. Pobell,J. Low Temp. Phys. 89, 465 (1992).
A. M. Guénault, V. Keith, C. J. Kennedy, and G. R. Pickett,Phys. Lett. 90A, 432 (1982).
see for example: Ref. 3, and D. J. Bradley, A. M. Guénault, V. Keith, C. J. Kennedy, J. E. Miller, S. G. Mussett, G. R. Pickett, and W. P. Pratt Jr.,J. Low Temp. Phys. 57, 359 (1984).
see for example: T. Nakayama inProg. in Low Temp. Phys., D. F. Brewer (ed.), Vol. XII, p. 115 (Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., 1989).
see for example: F. Pobell,Matter and Methods at Low Temperatures, (Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg 1992).
Ag, purity 5N, Goodfellow Metals, Cambridge, UK.
Ag sinter, nominal grain size 700 Å, Ulvac, Inabata Corp., Japan.
S. Brunauer, P. H. Emmett, and E. Teller,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 309 (1938).
K. Gloos, P. Smeibidl, C. Kennedy, A. Singsaas, P. Sekowski, R. M. Mueller, and F. Pobell,J. Low Temp. Phys. 73, 101 (1988).
R. J. Soulen and R. B. Dove,SRM 768: Temperature Reference Standard For Use Below 0.5 K; NBS Special Publication (1979).
M. Schwark, M. Kubota, R. M. Mueller, and F. Pobell,J. Low. Temp. Phys. 58, 171 (1985).
M. Schwark, F. Pobell, W. P. Halperin, Ch. Buchal, J. Hanssen, M. Kubota, and R. M. Mueller,J. Low Temp. Phys. 53, 685 (1983).
P. Esquinazi, R. König, and F. Pobell;Z, Phys. B — Cond. Matt. 87, 305 (1992); R. König, P. Esquinazi, and F. Pobell,J. Low Temp. Phys. 90, 55 (1993).
D. I. Bradley, A. M. Guénault, V. Keith, G. R. Pickett, and W. P. Pratt Jr.,J. Phys. C 30, L501 (1982).
H. Ishimoto, H. Fukuyama, N. Nishida, Y. Miura, Y. Takano, T. Fukuda, T. Tazaki, and S. Ogawa,J. Low Temp. Phys. 77, 133 (1989).
D. S. Greywall,Phys. Rev. B 33, 7520 (1986).
S. N. Fisher, G. R. Pickett, and R. J. Watts-Tobin,J. Low Temp. Phys. 83, 225 (1991).
A. M. Guénault, V. Keith, C. J. Kennedy, and G. R. Pickett,Proc. Symp. on Quantum Fluids and Solids, E. D. Adams, G. G. Ihas (eds.), p. 273, Sanibel Island, USA (1983).
A. M. Guénault, V. Keith, C. J. Kennedy, S. G. Mussett, and G. R. Pickett,J. Low Temp. Phys. 62, 511 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
König, R., Betat, A. & Pobell, F. Refrigeration and thermometry of liquid3He-4He mixtures in the ballistic regime. J Low Temp Phys 97, 311–333 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00752921
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00752921