Abstract
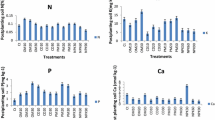
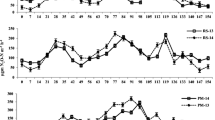
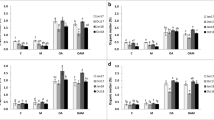
In a field study, the influence of organic mulches viz. paddy straw and citronella (Cymbopogon winterianus Jowitt) distillation waste on herb and essential oil yield and fertilizer N use efficiency in Japanese mint (Mentha arvensis L.) were examined for two years. Herb yield (dry weight) increased by 17 and 31% with paddy straw and citronella distillation waste, respectively over the use of no mulch. Essential oil yield also significantly increased due to mulching. A significant response to N was observed with 200 kg N ha−1 in unmulched plots as against 150 kg N ha−1 in mulched plots. Mulched soils have been observed to contain 2 to 4% higher moisture as compared to unmulched soils. Nitrogen uptake by plants increased by 18 and 25% over no mulch with using paddy straw and citronella distillation waste, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal SP, Gajri PR and Prihar SS (1971) Effect of mulches on water conservation, soil temperature and growth of maize (Zea mays Linn) and pearl millet [Pennisetum typhoides (Burm f.) Stapf & C.E. Hubb.]. Indian J Agric Sci 41: 467–473
Dutt R (1978) Soil temperature, soil moisture and straw mulch effects on N-mineralization and nitrification of soils and growth of forage maize. M.Sc. thesis PAU, Ludhiana, India
Jackson ML (1973) Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall of India Ltd., New Delhi
Khera KL, Singh B, Sandhu BS and Anjla TS (1986) Response of Japanese mint to nitrogen, irrigation and straw mulching on a sandy loam soil of Punjab. Indian J Agric Sci 56(6): 434–438
Patra DD, Anwar M, Sukhmalchand and Singh DV (1992) Fate of fertilizer15N applied as urea and ammonium sulphate in opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) grown under greenhouse conditions. Fert Res 32: 327–332
Singh DV, Yadav RL and Singh A (1982) Recent advances in research on essential oil bearing crops with reference to rural development in central U.P. Indian Perf 26: 90–93
Subbiah BV and Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the estimation of available N in soils. Curr Sci 25: 259
Yadav RL and Mohan R (1982) Physiological analysis of yield variation inMentha arvensis Linn. under different rates of N application. Indian Perf 26: 94–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patra, D.D., Ram, M. & Singh, D.V. Influence of straw mulching on fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency, moisture conservation and herb and essential oil yield in Japanese mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Fertilizer Research 34, 135–139 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750108
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750108