Abstract
Field experiments were conducted at Al-Qatif area in the eastern region of Saudi Arabia to study the status and availability of B under B fertilization regime in three types of calcareous soils and to evaluate the response of two alfalfa varieties, Hassawi (local variety) and Hyden (american variety), to increasing levels of added B.
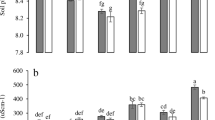
Boron was applied at 7 rates as Na2B4O7.10H2O. Four cuttings were taken from each site at different intervals. Data showed that extractable B by hot-water and NH4HCO3-DTPA (8 days after borax application) was significantly (p <0.001) affected by soil type and B applications. The amount of B recovered by hot-water from the three soils, 200 days after borax application, was in the following order: sandy loam > sandy clay loam > clay loam.
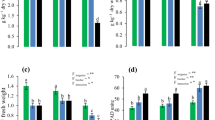
Total dry matter of alfalfa (4 cuttings) was significantly (p <0.05) affected by soil type, borax application rates and alfalfa variety.
The critical level of B in plant as determined by Cate and Nelson analysis, ranged from 148 to 652 mg kg−1 dry matter for Hassawi cultivar and 138 to 521 mg kg−1 for Hyden cultivar in the first harvest. However, the upper critical levels for the 2nd, 3rd and 4th harvests were 800, 875 and 935 mg B kg−1 dry matter for Hassawi and 603, 723 and 812 mg B kg−1 for Hyden varieties, respectively. Nevertheless, the lower critical levels for 2nd, 3rd and 4th harvests ranged from 148 to 153 mg B kg−1 dry matter for Hassawi and 138 to 142 mg B kg−1 for Hyden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger KC (1949) Boron in soils and crops. Adv Agron 1: 321–351
Berger KC and Truog E (1939) Boron determination in soils and plants. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 11: 540–544
Cate RB and Nelson LA (1971) A simple statistical procedure for partitioning soil test correlation data into two classes. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 35: 658–660
Cottrell NM (1975) Disposal of municipal wastes on sandy soils: Effect on plant nutrient uptake. M.S. thesis, Oregon State Univ. Corvallins
Dible WT, Truog E and Berger KC (1954) Boron determination in soils and plants: Simplified curcumin procedure. Anal Chem 26: 418–421
Dressen DR and Wanger L E (1981) Elemental composition of saltcedar (Tamarix chinensis) impacted by effluents from a coal-field power plant. J Environ Qual 10: 410–416
Eaton FM (1944) Deficiency, toxicity and accumulation of boron in plants. J Agric Res 94: 237–277
Fox RH (1968) The effect of calcium and pH on boron uptake from high concentrations of boron by cotton and alfalfa. Soil Sci 106: 435–439
Gestring WD and Soltanpour PN (1984) Evaluation of the ammonium bicarbonate-DTPA soil test for assessing boron availability to alfalfa. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 96–100
Gestring WD and Soltanpour PN (1987) Comparison of soil tests for assessing boron toxicity to alfalfa. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51: 1214–1219
Gupta UC (1967) A simplified method for determining hotwater soluble boron in podzol soils. Soil Sci 103: 424–428
Gupta UC (1972) Effects of boron and lime on boron concentration and growth of forage legumes under greenhouse conditions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 3: 355–365
Hortenstine CC, Ashley DA and Wear JI (1958) An evaluation of slowly soluble boron materials. Soil Sci Am Proc 22: 249–251
Keren R and Bingham FT (1985) Boron in water, soil and plant. In: Advances in soil sciences, Vol. 1, pp 229–276. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., New York
Khan ZD, Rayn J and Berger KC (1979) Available boron in calcareous soils of Lebanon. Agron J 71: 688–690
Lee SY, Dixon JB and Aba-Hussayn MM (1983) Minerology of Saudi Arabia soils: Eastern region. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47: 321–326
Lucas SW and Kenezenk BD (1972) Climatic and soil conditions promoting micronutrient deficiencies in plant. In: Mortvedt JJ (ed) Micronutrients in agriculture, pp 265–288. Soil Sci Soc Am Madison, WI
Melsted SW, Motto HL and Peck TR (1969) Critical plant nutrient composition values useful in interpreting plant analysis data. Agron J 61: 17–20
Ohaki K (1972) Lower and upper critical Zn levels in relation to cotton growth and development. Physiol Plant 35: 96–100
Ouellette GJ and LaChance RO (1954) Soil and plant analysis as a mean of diagnozing boron deficiency in alfalfa in Quebec. Can J Agric Sci 43: 494–503
Prather RJ (1977) Sulfuric acid as an amendment for reclaiming soils high in boron. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41: 1098–1101
Reisenauer HM, Walsh LM and Hoeft RG (1973) Testing soils for sulphur, boron, molybdenum and chlorine, In: Walsh LM and Beaton JD (eds) Soil testing and plant analysis, pp 173–200. Soil Sci Soc Am Madison, Wisconsin
SAS Institute (1988) SAS/STAT user's guide, Release 6.03 Edition. SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, NC
Shive JW (1941) Significant roles of trace elements in the nutrition of plants. Plant Physiol 16: 453–445
Wear JI and Patterson RM (1962) Effect of soil pH and texture on the availability of water-soluble boron in the soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 26: 344–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Mustafa, W.A., Falatah, A.M. & El-Shall, A.A. Effect of excess boron fertilization on status and availability of boron in calcareous soils. Fertilizer Research 36, 71–78 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749950
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749950