Abstract
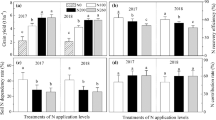
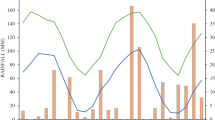
Yield response of dryland wheat to fertilizer N application in relation to components of seasonal water (available soil moisture and rainfall) and residual farm yard manure (FYM) was studied for five years (1983–84 to 1987–88) on a maize-wheat sequence on sandy loam soils in Hoshiarpur district of Punjab, India. Four rates of N viz. 0, 40, 60 and 80 kg ha−1 in wheat were superimposed on two residual FYM treatments viz. no FYM (F0) and 15 t ha−1 (F15) to preceding maize. FYM application to maize increased the residual NO3-N content by 19–30 kg ha−1 in the 180 cm soil profile. For a given moisture distribution, F15 increased attainable yields. Over the years, F15 increased wheat yield by 230 to 520 kg ha−1. Response to fertilizer N was lower in FYM amended plots than in unamended plots. Available soil moisture at wheat seeding and amount and distribution of rainfall during the vegetative and the reproductive phases of crop development affected N use efficiency by wheat. Available soil moisture at seeding alone accounted for 50% variation in yield. The residual effect of FYM on wheat yield could be accounted for by considering NO3-N in 180 cm soil profile at seeding. The NO3-N and available soil moisture at wheat seeding along with split rainfall for two main phases of crop development and fertilizer N accounted for 96% variation in wheat yield across years and FYM treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott JL and Tucker TC (1973) Persistence of manure phosphorus availability in calcareous soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 37: 60–63
Bauer A, Young RA and Ozburn JL (1965) Effects of moisture and fertilizer on yields of spring wheat and barley. Agron J 57: 354–356
Benbi DK (1990) Efficiency of nitrogen use by dryland wheat in a subhumid region in relation to optimizing the amount of available water. J Agric Sci (Camb) 115: 7–10
Biswas CR and Benbi DK (1989) Long term effects of manure and fertilizer on wheat based cropping systems in semi arid and alluvial soils. Fert News 34: 33–38
Bremner JM (1965) Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis 2, Agronomy 9, pp 1179–1237. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Eck HV (1988) Winter wheat response to nitrogen and irrigation. Agron J 80: 902–908
Eckert JB, Chaudhry NM and Qureshi SA (1978) Water and nutrient response of semi-dwarf wheat under improved management in Pakistan: Agronomic and economic implications. Agron J 70: 77–80
Engel RE (1991) Simulated growing season precipitation and nitrogen effects on winter wheat. Agron J 83: 180–185
Formoli GN and Parsad R (1979) Effect of farmyard manure and phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on soil properties in rice-wheat rotation. J Agric Sci (Camb) 92: 359–362
Grewal JS, Sharma RC and Sud KC (1981) Effect of continuous application of PK fertilizers and farmyard manure on potato yield and some soil properties. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 29: 129–131
Hanks RJ, Gardner HR and Florian RL (1969) Plant growth-evapotranspiration relations for several crops in the Central Great Plains. Agron J 61: 30–34
Hinman WC (1974) Effects of fertilizer and available moisture on the yield and N and P content of wheat and soil nutrients. Can J Soil Sci 54: 187–193
Jackson TL, Halvorson AD and Tucker BB (1983) Soil fertility in dryland agriculture. In: Dryland agriculture. Agron No. 23, pp 297–332. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Kanemasu ET, Stainer JL, Biere AW, Worman FD and Stone JF (1983) Irrigation in Great Plains. Agric Water Manage 7: 157–178
Kumar D, Rana DS and Kapur ML (1983) Economising fertilizer N through farm yard manure in maize (Zea mays L) in relation to dry matter production and N utilization. J Res Punjab Agric Univ 20: 293–301
Kumar D and Singh R (1985) Effect of farmyard manure on nitrogen use efficiency in maize-wheat sequence under rainfed conditions. Bull Indian Soc Soil Sci 13: 318–325
Mamchenkov IP and Vasilev VA (1972) Effectiveness of a combination of dung and mineral fertilizers in rotation. Agrokhimiya 5: 47–48
McIntosh JL and Varney KE (1972) Accumultive effects of manure and N on continuous corn on clay soil I. Growth, yield and nutrient uptake of corn. Agron J 64: 374–379
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS and Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available P extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circ No 939, USDA, Washington
Passioura JB (1983) Roots and drought resistance. Agric Water Manage 7: 265–280
Prihar SS, Gajri PR and Arora VK (1985) Nitrogen fertilization of wheat under limited water supplies. Fert Res 8: 1–8
Prihar SS and Hundal SS (1971) Determination of bulk density of soil clod by saturation. Geoderma 5: 283–286
Prihar SS, Sandhu KS, Singh M, Verma HN and Singh R (1989) Response of dryland wheat to small supplemental irrigation and fertilizer nitrogen in submontane Punjab. Fert Res 21: 23–28
Ramig RE and Rhoades HF (1963) Interrelationships of soil moisture level at planting time and nitrogen fertilization on winter wheat production. Agron J 55: 123–127
Read DWL and Warder FG (1974) Influence of soil and climatic factors on fertilizer response of wheat grown on stubble land in South-Western Saskatchewan. Agron J 66: 245–248
Singh R, Singh Y, Prihar SS and Singh P (1975) Effect of N fertilization on yield and water use efficiency of dryland wheat as affected by stored water and rainfall. Agron J 67: 599–603
Walkley A and Black CA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37: 29–38
Young RA, Ozbun JL, Bauer A and Vasey EH (1967) Yield response of spring wheat and barley to nitrogen fertilizer in relation to soil and climatic factors., Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 31: 407–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benbi, D.K., Singh, R., Singh, G. et al. Response of dryland wheat to fertilizer nitrogen in relation to stored water, rainfall and residual farm yard manure. Fertilizer Research 36, 63–70 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749949
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749949