Abstract
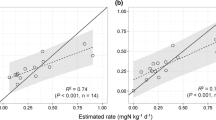
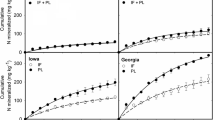
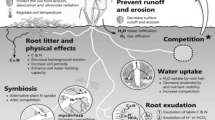
A pot incubation method for measuring mineralization dynamics from fresh plant material was tested. The aim was to develop a method which under well-defined conditions could produce mineralization data suited for estimating model input parameters for nitrogen prediction models. The results showed that the water tension of the soil could be controlled easily and precisely by diffusion through porous ceramic cups, and that nitrogen mineralization or immobilization could be measured already after 15 days at 15°C. The results showed that for the incubated catch crop residues carbon, nitrogen and nitrate-N contents were the most important factors determining mineralization. No significant effects ould be ascribed to other parameters measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrén O (1987) Decomposition of shoot and root litter of barley, lucerne and meadow, fescue under field conditions. Swedish J Agric Res 17: 113–122 AOAC (1965) Official methods of analysis. IOth ed. Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, Inc., USA
Bremer E, Houtum Wv and Kessel Cv (1991) Carbon dioxide evolution from wheat and lentil residues as affected by grinding, added nitrogen, and the absence of soil. Biol Fertil Soils 11: 221–227
Elers B and Hartmann HD (1987) Biologische konservierung von Nitrat. Gemüse 4: 210–214
Fox RH, Myers RJK and Vallis I (1990) The nitrogen mineralization rate of legume residues in soil as influenced by their polyphenol, lignin, and nitrogen contents. Plant and Soil 129: 251–259
Frank ZR, Verhaegh WB and Bakker JW (1991) The effect of constant moisture and aeration levels in soil on Fusarium wilt in tomatoes. Plant and Soil 136: 231–238
Frankenberger WT and Abdelmagid (1985) Kinetic parameters of nitrogen mineralization rates of leguminous crops incorporated into soil. Plant and Soil 87: 257–271
Hansen S, Jensen HE, Nielsen NE and Svendsen H (1991) Simulation of nitrogen dynamics and biomass production in winter wheat using the Danish simulation model DAISY. Fert Res 27: 245–259
Ito O and Watanabe I (1985) Availability to rice plants of nitrogen fixed by azolla. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 31: 91–104
Jingguo W and Bakken LR (1989) Nitrogen mineralization in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil, effect of spatial distribution of N-rich and N-poor plant residues.In Nitrogen in (organic wastes applied to Soils, Hansen JA and Henriksen K (eds)Academic Press pp: 61–97.
SAS INSTITUTE (1988 SAS/STAT Users Guide, Release 6.03 Edition. SAS Institute Inc.
Ladd JN, Jocteur-Monrozier L and Amato M (1992) Carbon turnover and nitrogen transformations in an alfisol and vertisol amended with [U-14C] glucose and [15N] ammonium sulfate. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 359–371
Marstorp H and Kirchmann H (1991) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization and crop uptake of nitrogen from six green manure legumes (lecomposing in soil. Acta Agric Scand 41: 243–252
Neely CL, Beare MH, Hargrove WL and Coleman DC (1991) Relationships between fungal and bacterial substrate-induced respiration, biomass and plant residue decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 23: 947–954
Oglesby KA and Fownes JH (1992) Effects of chemical composition on nitrogen mineralization form green manure of seven tropical leguminous trees. Plant and Soil 143: 127–132
Paustian K, Parton WJ and Persson J (1992) Modelling soil organic matter in organic-amended and nitrogen-fertilized long-term plots. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56: 476–488
Sims JL and Fredrick LR (1970) N immobilization and decomposition of corn residues in soil and sand as affected by residue particle size. Soil Sci 109: 355–361
Sørensen JN and Thorup-Kristensen K (1993) Nitrogen effects of non-legume catch crops. Z Pflanzenemahr Bodenkd 156: 55–59
Thorup-Kristensen K (1993) The effect of nitrogen catch crops on the nitrogen nutrition of a succeeding crop I: Effects through mineralization and pre-emptive competition. Acta Agric Scand, Sect B Soil and Plant Sci 43: 74–81
Thorup-Kristensen K (1994) The effect of nitrogen catch crop species on the nitrogen nutrition of a succeeding crop. Fert Res 37: 231–239
Tilley JMA and Terry A (1963) A two stage lechnique for the digestion of forage crops. J Britt Grassld Soc 18: 104–111
Van Soest PJ (1963) Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. J AOAC 46: 825–835
Verberne ELJ, Hassink J, Willigen P De, Groot JJR and Veen JA van (1990) Modelling organic matter dynamics in different soils. Neth J Agric Sci 38: 221–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thorup-Kristensen, K. An easy pot incubation method for measuring nitrogen mineralization from easily decomposable organic material under well defined conditions. Fertilizer Research 38, 239–247 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749697
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749697