Abstract
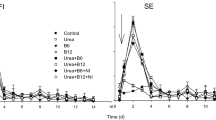
Ammonia volatilization from urea, diammonium phosphate, ammonium sulphate and calcium ammonium nitrate surface applied to winter wheat and grassland was determined with windtunnels. The fertilizers were applied at a rate of 8–12 g N m−2 to plots on a non-calcareous sandy loam. Five experiments were carried out during March to June 1992, each experiment including 2 to 4 treatments with two or three replications. The daily ammonia loss rate was measured during 15 to 20 days. Cumulated daily loss of ammonia from urea followed a sigmoidal expression, while the cumulated ammonia loss from diammonium phosphate showed a logarithmic relationship with time from application. For ammonium sulphate and calcium ammonium nitrate no significant loss could be determined, because daily loss of ammonia were at the detection limit of the wind tunnels. Mean cumulated ammonia loss from plots receiving urea, diammonium phosphate, ammonium sulphate and calcium ammonium nitrate were 25%, 14%, <5% and <2%, respectively, during a 15–20 day measuring period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asman WAH and Runge EH (1991) Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen compounds in Denmark. In: Nielsen MD (ed.) Proceedings from International Conference on Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Organic Matter. DK-Helsingør, May 13–15 1991, pp. 287–312. Miljøstyrelsen, Copenhagen, Denmark
Asman WAH (1992) Ammonia emission in Europe: Updated emission and emission variations. RIVM National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Protection. Report no. 228471008, p. 88
Buijsman E, Maas HFM and Asman WAH (1987) Anthropogenic NH3 emissions in Europe. Atmos Environ 21: 1009–1022
Black AS, Sherlock RR, Cameron KC, Smith NP and Goh KM (1985) Comparison of three field methods for measuring ammonia volatilization from urea granules broadcast on to pasture. J Soil Sci 36: 271–280
Christensen BT and Sommer SG (1989) Fordampning af ammoniak fra udbragt gødning. Metode og ammoniaktab fra urea og urea-ammonium-nitrat. Volatilization of ammonia from fertilizers and manure. Methodology and loss of ammonia from urea and urea-ammonium-nitrate. (Summary and legends in English). Tidsskr Planteavl 93: 177–190
Crooke WM and Simpson WE (1971) Determination of ammonium in Kjeldahl digests of crops by an automated procedure. J Sci Food Agric 22: 9–10
Fenn LB and Kissel DE (1973) Ammonia volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils. I. General Therory. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 37: 855–859
Fenn LB and Hossner LR (1985) Ammonia volatilization from ammonium or ammonium-forming nitrogen fertilizers. Adv Soil Sci 1: 123–167
Ferguson RB, McInnes KJ, Kissel DE and Kanemasu ET (1988) A comparison of methods of estimating ammonia volatilization in the field. Fert Res 15: 55–69
Hunt R (1982) Plant growth curves. The functional approach to plant growth analysis. Edward Arnold Ltd. London, UK.
Klaasen G (1990) Emissions of ammonia in Europe. Report from IIASA, A-2361 Laxenburg Austria, WP-90-68, p. 39
Larsen S and Gunary D (1962) Ammonia loss from ammoniacal fertilizers applied to calcareous soils. J Sci Food Agric 13: 566–572
Lockyer, DR (1984) A system for the measurement in the field of losses of ammonia through volatilization. J Sci Food Agric 35: 837–848
McInnes KJ, Ferguson RB, Kissel DE and Kanemasu ET (1986) Field measurements of ammonia loss from surface applications of urea solution to bare soil. Agron J 78: 192–196
Olesen JE and Sommer SG (1993) Modelling effects of wind speed and surface cover on ammonia volatilization from stored pig slurry. Atmos Environ (in press)
Reynolds CM and Wolf DC (1987) Effect of soil moisture and air relative humidity on ammonia volatilization from surface applied urea. Soil Sci 143: 144–152
Roelofs JGM, Kempers AJ, Houdjik ALFM and Jansen J (1985) The effect of air-borne ammonium sulphate on Pinus Nigra var. maritima in the Netherlands. Plant Soil 84: 45–56
Ryden JC and Lockyer DR (1985) Evaluation of a system of wind tunnels for field studies of ammonia loss from grassland through volatilization. J Sci Food Agric 36: 781–788.
Ryden JC, Whitehead DC, Lockyer DR, Thompson RB, Skinner JH, and Garwood EA (1987) Ammonia emission from grassland and livestock productions systems in the UK. Environ Pollut 46: 173–184
SAS/STAT User's Guide (1988) Release 6.03 Edition, SAS Institute Inc.
Schulze E-D, Vries W De, Hauhs M, Rosén K, Rasmussen L, Tamm CO and Nilsson J (1989) Critical loads for nitrogen deposition on forest ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut 48: 451–456
Sommer SG, Olesen JE and Christensen BT (1991) Effects of temperature, wind speed and air humidity on ammonia volatilization from surface applied cattle slurry. J Agric Sci Camb 117: 91–100
Sommer SG and Ersbøll AK (1993) Ammonia volatilization from surface applied ammoniacal fertilizers: Effect of air flow rate and characteristics of light soils from long term experiments with and without lime amendments (in preparation)
Stevens RJ, Laughlin RJ and Kilpatrick DJ (1989) Soil properties related to the dynamics of ammonia volatilization from urea applied to the surface of acidic soils. Fert Res 20: 1–9
Velthof GL, Oenema O, Postmus J and Prins WH (1990) Insitu field measurements of ammonia volatilization from urea and calcium ammonium nitrate applied to grassland. Meststoffen 1/2: 41–45
Whitehead DC and Raistrick N (1990) Ammonia volatilization from five compounds used as fertilizers following surface application to soils. J Soil Sci 41: 387–394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sommer, S.G., Jensen, C. Ammonia volatilization from urea and ammoniacal fertilizers surface applied to winter wheat and grassland. Fertilizer Research 37, 85–92 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00748549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00748549