Abstract
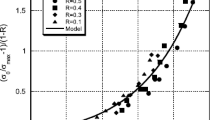
Strength and fatigue of multicomponent glass fibres have been measured as a function of environment and glass composition. Strength and dynamic fatigue were measured using a two-point bending technique from − 196 to 100‡ C and also in vacuo down to 10−5 torr. Zero stress ageing and static fatigue have been measured in ambient air and water at 20‡ C for different glass compositions. The addition of zinc, magnesium and aluminium oxides to sodium borosilicate glasses were shown to give significant improvements to the corrosion behaviour and a glass has been developed which could survive in water for longer than 7×103 h at strains greater than 1%. Finally a modified theory of static fatigue has been outlined in order to explain the departure from conventional stress corrosion theory that was evident in some glass compositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. J. Beales, C. R. Day, A. G. Dunn andS. Partington,Proc. IEEE 10 (1980) 1191.
K. J. Beales, C. R. Day, W. J. Duncan, A. G. Dunn, P. L. Dunn andG. R. Newns,Phys. Chem. Glasses 21 (1980) 25.
P. W. France, W. J. Duncan andK. J. Beales, Proceedings of the 12th International Congress on Glass, Albuquerque, 1980 (North-Holland, Amsterdam).
J. E. Ritter,Fiber Int. Optics 1 (1978) 387.
W. J. Duncan, P. W. France andK. J. Beales, Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Optical Fibre Communication, Copenhagen, 1981 (Peter Peregrinus, Stevenage).
P. W. France, P. L. Dunn andM. H. Reeve,Fiber Int. Optics 2 (1979) 267.
P. W. France, M. J. Paradine, M. H. Reeve andG. R. Newns,J. Mater. Sci. 15 (1980) 825.
S. M. Weiderhorn andL. H. Bolz,J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 53 (1970) 543.
L. L. Hench,J. Non-cryst. Solids 19 (1975) 27.
S. Shibata, S. Takahashi, S. Mitachi andM. Yasu,ibid. 43 (1981) 79.
D. KalishandB. K. Tariyal,J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 61 (1978) 518.
Idem, Appl. Phys. Lett. 28 (1976) 721.
C. K. Kao, “Optical Fibre Communications” (John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester 1980) p. 241.
J. T. Krause, Proceedings of the 12th International Congress on Glass, Albuquerque, 1980 (North-Holland, Amsterdam) p. 497.
A. G. Evans andS. M. Weiderhorn,Int. J. Fract. 10 (1974) 379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
France, P.W., Duncan, W.J., Smith, D.J. et al. Strength and fatigue of multicomponent optical glass fibres. J Mater Sci 18, 785–792 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00745577
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00745577