Summary
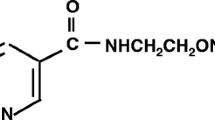
The possible interaction between amiodarone, a potent antiarrhythmic and antianginal agent, and calmodulin (CaM) was investigated by three avenues of approach: (a) Effect of amiodarone on cardiac and vascular Ca2+/calmodulin-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (CaM-PDE); (b) Effect on the CaM-activated (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from human erythrocytes; (c) Direct interaction between amiodarone and calmodulin measured by the effect of the drug on the fluorescence of 9-anthroylcholine (9AC) bound to calmodulin. Results show that amiodarone did not interact with basal activities of CaM-PDE and other isolated CaM-insensitive PDE forms as well as with (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Amiodarone inhibited calmodulin-activation of aortic CaM-PDE (K i = 650 nM, substrate cGMP) and calmodulin-activation of erythrocyte ghosts (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase (IC50 = 4.5 μM) in an apparently competitive manner. Amiodarone decreased the fluorescence of the hydrophobic probe 9AC bound to calmodulin (IC50 = 5 μM).
It is concluded that amiodarone is a potent calmodulin antagonist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P, Virshup D, Bennett V (1984) Bepridil and cetiedil: vasodilators which inhibit Ca2+-dependent calmodulin interactions with erythrocytes membranes. J Clin Invest 74:812–820
Anno T, Kodama y, Shibata S, Toyama J, Yamada K (1986) Effects of calcium, calcium entry blockers and calmodulin inhibitors on atrio-ventricular conduction disturbances induced by hypoxia. Br J Pharmacol 88:277–284
Baginski ES, Foa PP, Zak B (1967) Determination of phosphate: study of labile organic phosphate interference. Clin Chim Acta 15:155–158
Beresewicz A, Karwatowska-Krynska E (1986) Effect of calmodulin antagonists on hypoxia and reoxygenation damage in isolated rabbit hearts. Basic Res Cardiol 81:311–325
Bostrom SL, Ljung B, Mardh S, Forsens S, Thulin E (1981) Interactions of the antihypertensive drug felodipine with calmodulin. Nature 292:777–778
Broekhuysen J, Clinet M, Delisée C (1972) Action of amiodarone on guinea pig heart sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem Pharmacol 21:2951–2960
Charlier R, Deltour G, Baudine A, Chaillet F (1968) Pharmacology of amiodarone, an anti-anginal drug with a new biological profile. Arzneim Forsch (Drug Res) 18:1408–1417
Chatelain P, Laruel R (1985) Amiodarone partitioning with phospholipid bilayers and erythrocyte membranes. J Pharmacol Sci 74:783–784
Chatelain P, Laruel R, Gillard M (1985) Effect of amiodarone on membrane fluidity and Na+/K+ ATPase activity in rat brain synaptic membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 129:148–154
Cohen-Armon M, Schreiber G, Sokolowski M (1984) Interaction of the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone with the muscarinic receptor of rat heart and brain. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6:1148–1155
Cote P, Bourassa M, Delaye J, Janin A, Froment R, David P (1979) Effects of amiodarone on cardiac and coronary hemodynamics and on myocardial metabolism in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 59:1165–1172
Downes P, Michell RH (1981) Human erythrocyte membranes exhibit a cooperative calmodulin-dependent Ca2+-ATPase of high calcium sensitivity. Nature 290:270–271
Edoute Y, Van der Merwe EL, Sanan D, Kotze JCN (1983) Normothermic ischaemic cardiac arrest and reperfusion of the isolated working heart: effect of chlorpromazine on functional, metabolite and morphological recovery. J Mol Cell Cardiol 15:603–620
Epstein PM, Fiss K, Hachisu R, Andrenyak DM (1982) Interaction of calcium antagonists with cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase and calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 105:1142–1149
Ferreira J, Brasseur R, Chatelain P, Ruysschaert JM (1986) Properties of amiodarone monolayer spread at the air-water interface. J Pharm Pharmacol 38:561–566
Follenius A, Gerard D (1984) Fluoresence investigations of calmodulin hydrophobic sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119:1154 -1160
Gagnol JP, Devos C, Clinet M, Nokin P (1985) Amiodarone: biochemical aspects and hemodynamic effects. Drugs 29 (Suppl 3):1–10
Hait WN, Lee GL (1985) Characteristics of the cytotoxic effects of the phenothiazine class of calmodulin antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 34:3973–3978
Heath MF, Costa-Jussà FR, Jacobs JM, Jacobson W (1985) The induction of pulmonary phospholiposis and the inhibition of lysosomal phospholipases by amiodarone. Br J Exp Path 66:391- 397
Hidaka H, Tanaka T (1983) Naphthalenesulfonamides as calmodulin antagonists. Meth Enzymol 102:185–194
Holt D, Tucker G, Jackson P, Storey G (1983) Amiodarone pharmacokinetics. Am Heart J 106:840–847
Hostetler KY, Reasor MJ, Walker ER, Yazaki PJ, Frazee PW (1986) Role of phospholipase A inhibition in amiodarone pulmonary toxicity in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 975:400–408
Isobe T, Nakajima T, Okuyama T (1977) Reinvestigation of extremely acid proteins in bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Acta 194:222–232
Itoh H, Ishikama T, Hidaka H (1984) Effect on calmodulin of bepridil, an antianginal agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230: 737–741
Johnson JD, Wittenauer LA (1983) A fluorescent calmodulin that reports the binding of hydrophobic inhibitory ligands. Biochem J 211:473–479
Kosinski EJ, Albin JB, Young E, Lewis SM, Leland OS (1984) Hemodynamic effects of intravenous amiodarone. J Am Coll Cardiol 4:565–570
Kubo K, Matsuda Y, Kase H, Yamada K (1986) Inhibition of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by flunarizine, a calcium entry blocker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 124:315–321
Lamers JMJ, Cysouw KJ, Verdouw PD (1985) Slow calcium channel blockers and calmodulin: effect of felodipine, nifedipine, prenylamine and bepridil on cardiac sarcolemmal calcium ATPase. Biochem Pharmacol 34:3837–3843
Levine SN, Berkowitz LR, Orringer EP (1984) Cetiedil inhibition of calmodulin-stimulated enzyme activity. Biochem Pharmacol 33:581–584
Luchowski EM, Youssif F, Triggle DJ, Maurer SC, Sarmiento JG, Janis RA (1984) Effects of metal cations and calmodulin antagonists on3H-nitrendipine binding in smooth and cardiac muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:607–613
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lugnier C, Follenius A, Gerard D, Stoclet JC (1984) Bepridil and flunarizine as calmodulin inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol 98:157–158
Lugnier C, Schoeffter P, Le Bee A, Strouthou E, Stoclet JC (1986) Selective inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of human, bovine and rat aorta. Biochem Pharmacol 35:1743–1751
Marcus FI, Fontaine GH, Franck R, Grosgogeat T (1981) Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic applications of the anti-arrhythmic agent, amiodarone. Am Heart J 101:480–493
Nokin P, Clinet M, Schoenfeld P (1983) Cardiac \-adrenoceptor modulation by amiodarone. Biochem Pharmacol 32:2473–2477
Nokin P, Clinet M, Swillens S, Delisée C, Meysmans L, Chatelain P (1986) Allosteric modulation of [3H]-nitrendipine binding to cardiac and cerebral cortex membranes by amiodarone. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 8:1051–1057
Nokin P, Jungbluth L, Mouton J (1987) Protective effects of amiodarone pretreatment on mitochondrial function and high energy phosphates in ischaemic rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 19:603–614
Polster P, Broekhuysen J (1976) The adrenergic antagonism of amiodarone. Biochem Pharmacol 25:131–134
Prozialeck WC, Weiss B (1982) Inhibition of calmodulin by phenothiazines and related drugs: Structure-activity relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 222:509–516
Reynolds CH, Claxton PTJ (1982) Inhibition of calmodulin-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase: multiple binding-sites for tricyclic drugs on calmodulin. Biochem Pharmacol 31:419–421
Robertson S, Potter JD (1984) The regulation of free Ca+ ion concentration by metal chelators. In: Schwartz A (ed) Methods in pharmacology, vol 5. Plenum Press, New York, pp 63–75
Schaeffer P, Lugnier C, Follenius-Wund A, Gerard D, Stoclet JC (1987) Comparative effects of calmodulin inhibitors on calmodulin's hydrophobic sites and on the activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by calmodulin. Biochem Pharmacol 36:1989–1996
Schiefer S (1986) Calmodulin. In: Bergmeyer (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 9. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 317–331
Schwertschlag U, Schrier RW, Wilson P (1986) Beneficial effects of calcium channel blockers and calmodulin binding drugs on in vitro renal cell anoxia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:119–124
Tkachuk VA, Baldenkov GN, Feoktistov IA, Men'shikov MY, Quast U, Herzig JW (1987) Metofenazate as a more selective calmodulin inhibitor than trifluoperazine. Arzneim Forsch (Drug Res) 37:1013–1017
Van Belle H (1981) R 24571: a potent inhibitor of calmodulinactivated enzymes. Cell Calcium 2:483–494
Weiss B, Prozialeck WC, Wallace TL (1982) Interaction of drugs with calmodulin: biochemical, pharmacological and clinical implications. Biochem Pharmacol 31:2217–2226
Wells JN, Baird CE, Wu YJ, Hardman JG (1975) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities of pig coronary arteries. Biochim Biophys Acta 384:430–442
Zimmer WN, Hoffmann J (1987) Differentiation of the drug binding sites of calmodulin. Eur J Biochem 164:411–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nokin, P., Blondiaux, J.P., Schaeffer, P. et al. Amiodarone is a potent calmodulin antagonist. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 339, 367–373 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00736049
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00736049