Abstract
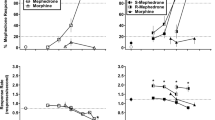
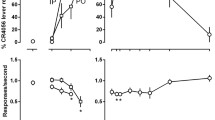
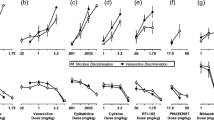
Rats were trained to discriminate clozapine (CLZ; 5.76 mg/kg, IPt-30 min) in a two-lever operant task in which responding on the correct lever was reinforced with water under a fixed ratio 32 schedule. The ED50 of CLZ was 1.1 mg/kg. The CLZ cue was generalised to atropine (ED50=8.7 mg/kg), scopolamine (ED50=0.37 mg/kg) and fluperlapine (ED50=4.0 mg/kg), but not to non-cholinergic compounds, i.e. buspirone, diazepam, ketanserin, prazosin or SCH 23390. The peripherally-acting muscarinic antagonist methylscopolamine did not substitute for CLZ. Furthermore, the CLZ cue was marginally attenuated byd-amphetamine; a high dose of oxotremorine (1 mg/kg) appeared to block the CLZ cue (to 22%). However, this effect could not be evaluated statistically due to an insufficient number of animals responding. These results may indicate that the discriminative stimulus effects of CLZ primarily involve antagonism of central muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen PH, Grønvald FC (1986) Specific binding of3H-SCH 23390 to dopamine D-1 receptors in vivo. Life Sci 38:1507–1514
Browne RG, Koe BK (1982) Clozapine and agents with similar behavioral and biochemical properties. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JF (eds) Drug discrimination: applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 241–256
Colpaert FC, Slangen JF (1982) Drug discrimination: applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam
Eichenberger E (1984) Pharmacology of fluperlapine compared with clozapine. Drug Res 34:110–113
Evans T, Hepler JR, Masters SB, Brown JH, Harden TK (1985) Guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding to muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Biochem J 232:751–757
Gerlach J, Thorsen K, Fog R (1975) Extrapyramidal reactions and amine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid during haloperidol and clozapine treatment of schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacologia 40:341–350
Goas J, Boston JE (1978) Discriminative stimulus properties of clozapine and chlorpromazine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:235–241
Janssen PAJ (1983) 5-HT2 receptor blockade to study serotonin-induced pathology. TIPS 4:198–206
Kubena RK, Barry H III (1969a) Generalization by rats of alcohol and atropine stimulus characteristics to other drugs. Psychopharmacologica 15:196–206
Luthin GR, Wolfe BB (1985) Characterization of3H-pirenzepine binding to muscarinic cholinergic receptors solubilized from rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:37–44
Meltzer LT, Rosecrans JA (1981) Discriminative stimulus properties of arecoline: a new approach for studying central muscarinic receptors. Psychopharmacology 75:383–387
Miller RJ, Hiley CR (1974) Antimuscarinic properties of neuroleptics and drug-induced Parkinsonism. Nature 248:596–597
Moore NA, Tye NC, Risius FC, Pullar IA (1984) The discriminative stimulus properties of clozapine. Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum 14th Int. Congress (Abstract) p 816
Nielsen EB, Jepsen SA (1985) Antagonism of the amphetamine cue by both classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 111:167–176
Niemegeers CJE, Colpaert FC, Leysen JE, Awouters F, Janssen PAJ (1983) Mescaline-induced head-twitches in the rat: an in vivo method to evaluate serotonin S2-antagonists. Drug Dev Res 3:123–135
Ortmann R, Meisburger JG, Bischoff S, Hanser K, Bittiger H, Waldmeier PC (1986) The clozapine cue in rats as tool for characterization of neuroleptics. Psychopharmacology 89:s47
Overton D (1982) Comparison of the degree of discriminability of various drugs using the T-maze drug discrimination paradigm. Psychopharmacology 76:385–395
Overton DA (1977) Discriminable effects of anti-muscarinics: Dose response and substitution test studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:659–666
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1980) Relationship of neuroleptic drug effects at brain dopamine, serotonin and α-adrenergic and histamine receptors to clinical potency. Am J Psychiatry 137:1518–1522
Snyder SH, Greenberg P, Yamamura HI (1974) Antischizophrenic drugs and brain cholinergic receptors. Arch Gen Psychiatry 31:58–61
Weiner N (1980) Atropine, scopolamine and related antimuscarinic drugs. In: Goodman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. McMillan, New York, pp 120–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, E.B. Cholinergic mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of clozapine. Psychopharmacology 94, 115–118 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735891
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735891