Summary
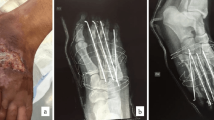
Between the years 1985–1988, 32 patients with wringer injury of the upper extremity were admitted to our institution. A uniform treatment program was carried out on all patients; this included aseptic wound care, immobilization and elevation of the involved extremity and early coverage of skin defects. The important aspects in the management of wringer injuries are reviewed, and the importance of early coverage of skin defects is emphasized. Furthermore, it was concluded that the surface area of deep ecchymosis measured 48 h after injury was useful as a simple and objective criterion to estimate the extent of final skin necrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JP, Fowler FD (1959) Wringer injuries of the upper extremity. South Med J 42:798
Allen JE, Beck AR, Jewett TC (1968) Wringer injuries in children. Arch Surg 97:194
Archer RR, Sawyers JL (1968) Surgical management of wringer arm injuries. South Med J 61:975
Cabbabe EB, Stanley WK (1983) Wringer washer injuries in children. Ann Plast Surg 10:135
Chamberlain JW, Soltes M (1961) Wringer injuries. Pediatrics 28:96
Entin MA (1955) Roller and wringer injuries: clinical and experimental studies. Plast Reconstr Surg 15:290
Golden GT, Fisher JC, Edgerton MR (1973) Wringer arm reevaluated: a survey of current surgical management of upper extremity compression injuries. Ann Surg 177:362
Hausmann PF, Everett HH (1950) Wringer injury. Surgery 28:71
Iritani RI, Siler VE (1961) Wringer injuries of the upper extremity. Surg Gynecol Obstet 113:677
Luck JV, Maddox R (1955) Washing machine wringer injuries in children. GP 12:87
MacCollum DW (1938) Wringer arm. N Engl Med J 218:549
MacCollum DW, Bernhard WF, Banner RL (1952) The treatment of wringer arm injuries. N Engl J Med 247:750
McCulloch JH, Boswick JA, Jonas R (1973) Household wringer injuries: a three-year review. J Trauma 13:1
McGee GE, Groff DB (1983) Wringer injuries of extremities. South Med J 76:304
Paulos E (1958) The open treatment of wringer injuries in children. Am Surg 24:458
Schulz I (1946) Wringer injury. Surgery 20:301
Thompson HG, Hampole MK (1970) Monkey-hand wringer injury. Plast Reconstr Surg 45:471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sensoz, O., Mutaf, M., Kocer, U. et al. The management of wringer injuries. Eur J Plast Surg 14, 168–172 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00734420
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00734420