Abstract
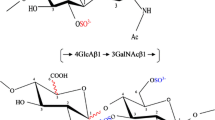
Novel sulfated and nonsulfated oligosialyglycosphingolipids were isolated from sperm of the sea urchin,Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus, and their structures were established as follows: ±HSO3→Neu5Acα2→(8Neu5Acα2→)n→6G1cβ1→1´Cer, wheren=0, 1, 2, 3. This provides the first evidence for the natural occurrence of a tetrasialic acid structure in glycosphingolipids. The finding of sulfated oligosialyl chains is especially noteworthy in that the sulfate group exclusively resides on the C-8 of the nonreducing terminal residues of oligo/polysialyl chains and that sulfation appears to be a termination signal for elongation of oligosialyl chains. Sulfation at the nonreducing terminal Neu5Ac residues of oligosialyl chains was also found to facilitate the formation of an inter-residue lactone between the carboxyl group at the nonreducing terminal sulfated Neu5Ac and the hydroxyl group at C-9 of the penultimate Neu5Ac residue. The long chain base was 4-hydroxysphinganine (t18:0) and the major fatty acid species were identified as C20:1, C21:1, and C22:1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C:M:
-
chloroform:methanol
- FAB-MS:
-
fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry
- GLC:
-
gas-liquid chromatography
- GSL:
-
glycosphingolipid
- HPTLC:
-
high performance thin-layer chromatography
- Neu5Ac8HSO3 or HSO3 → Neu5Ac:
-
5-N-acetyl-8-O-sulforylneuraminic acid
- Neu5Gc9HSO3 :
-
5-N-glycolyl-9-O-sulforylneuraminic acid
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- PB:
-
sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.2
- Sia:
-
sialic acid
- HSO3 → Sia:
-
sulfated sialic acid
- polySia:
-
polysialic acid
- TFA:
-
trifluoroacetic acid
References
Kitazume S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Troy FA II, Cho J-W, Lennarz WJ, Inoue Y (1994)J Biol Chem 269: 22712–18.
Inoue S, Iwasaki M (1978)Biochem Biophys Res Commun 83: 263–68.
Nadano D, Iwasaki M, Endo S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Inoue Y (1986)J Biol Chem 261: 11550–57.
Yu S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Inoue Y (1991)J Biol Chem 266: 21929–35.
Yu S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Muto Y, Kasama T, Handa S, Inoue Y (1993)Biochemistry 32: 9221–29.
Yu S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Khoo K-H, Dell A, Inoue Y (1995)Glycobiology 5: 207–18.
Hoshi M, Nagai Y (1975)Biochim Biophys Acta 388: 152–62.
Kochetkov NK, Smirnova GP, Chekareva NV (1976)Biochim Biophys Acta 424: 274–83.
Prokazova NV, Mikhailov G, Bergelson LD (1981)Eur J Biochem 115: 671–77.
Angata T, Kitazume S, Terada T, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Troy FA II, Inoue Y (1994)Glycoconjugate J 11: 493–99.
Kitazume S, Kitajima K, Inoue S, Haslam SM, Morris HR, Dell A, Lennarz WJ, Inoue Y (1995)Glycoconjugate J 12: 511.
Folch J, Lees M, Sloan-Stanley GH (1957)J Biol Chem 226: 497–509.
Svennerholm L (1957)Biochim Biophys Acta 24: 604–11.
Nomoto H, Iwasaki M, Endo T, Inoue S, Inoue Y, Matsumura G (1982)Arch Biochem Biophys 218: 335–41.
Yu RK, Ledeen RW (1970)J Lipid Res 11: 506–16.
Anumula KR, Taylor PB (1992)Anal Biochem 203: 101–8.
Inoue S, Matsumura G, Inoue Y (1982)Anal Biochem 125: 118–24.
Dell A, Reason AJ, Khoo K-H, Panico M, McDowell RA, Morris HR (1994)Methods Enzymol 230: 108–32.
Ando S, Yu RK, Scarsdale JN, Kusunoki S, Prestefard JH (1989)J Biol Chem 264: 3478–83.
Koerner TAW, Pretegard JH, Demow PC, Yu RA (1984)Biochemistry 22: 2676–98.
Iwasaki M, Inoue S, Kitajima K, Nomoto H, Inoue Y (1984)Biochem Int 8: 573–79.
Ishizuka I, Wiegandt H (1972)Biochim Biophys Acta 260: 279–89.
Ando S, Yu RK (1979)J Biol Chem 254: 12224–29.
Rösnor H (1993) inPolysialic Acid (Roth J, Rutishauser U, Troy FA, eds) pp. 279–97, Basel, Switzerland: Birkhuäser Verlag.
Kochetkov NK, Smirnova GP (1986)Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 44: 387–438.
Tanphaichitr N, Smith J, Mongkolsirikieart S, Gradil C, Lingwood CA (1993)Dev Biol 156: 164–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Since the dividing line between oligo- and polysialic acids is not rigidly defined, we propose here that those containing more than penta-sialic acid chains can be referred to as the polysialic acid group. The rationale for this is that α2 → 8-linked pentasialic acid is the minimum chain length to exhibit the conformational property of polysialic acid [of Michon, F, Brisson, J-R, Jennings, H (1987)Biochemistry 26: 8399–405] and to act as a substrate for the endosialidase, Endo-N [Hallenbeck, PC, Vimr, ER, Yu, F, Bassler, B, Troy, FA (1987)J Biol Chem 262: 3553–61].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ijuin, T., Kitajima, K., Song, Y. et al. Isolation and identification of novel sulfated and nonsulfated oligosialyl glycosphingolipids from sea urchin sperm. Glycoconjugate J 13, 401–413 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731473
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731473