Abstract
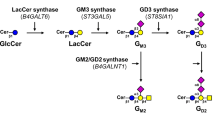
The aim of the present study was to investigate the ganglioside expression of the highly metastatic murine lymphoreticular tumour cell line MDAY-D2. Cells were propagated under controlled pH conditions and oxygen supply in bioreactors of 1 and 7.5l volumes by repeated batch fermentation. Gangliosides were isolated from 2.7×1011 cells, purified by silica gel chromatography and separated into mono- and disialoganglioside fractions by preparative DEAE anion exchange high performance liquid chromatography. Individual gangliosides were obtained by preparative thin layer chromatography. Their structural features were established by immunostaining, fast atom bombardment and gas chromatography mass spectrometry. In addition to gangliosides of the GM1a-pathway (GM2, GM1a and GD1a) and GM1b (IV3Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer) and GalNAc-GM1b of the GM1b-pathway, the dis8aloganglioside GD1α (IV3Neu5Ac, III6Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer) was found in equal amounts compared to GD1a (IV3Neu5Ac, II3Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer). All gangliosides were substituted with C24:0,24:1 and C16:0 fatty acids, sphingosine andN-acetylneuraminic acid as the sole sialic acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakomori S (1981)Ann Rev Biochem 50:733–64.
Hakomori S (1985)Cancer Res 45:2405–14.
Yogeeswaran G, Salk PL (1981)Science 212:1514–16.
Dyatlovitskaya EV, Bergelson LD (1987)Biochim Biophys Acta 907:125–43.
Dennis JW (1986)Cancer Res 46:4594–600.
Murayama K, Levery SB, Schirrmacher V, Hakomori S (1986)Cancer Res 46:1395–402.
Hanisch FG, Sölter J, Jansen V, Lochner A, Peter-Katalinié J, Uhlenbruck G (1990)Br J Cancer 61:813–20.
Laferté S, Fukuda MN, Fukuda M, Dell A, Dennis JW (1987)Cancer Res 47:150–9.
Müthing J, Peter-Katalinié J, Hanisch FG, Neumann U (1991)Glycoconjugate J 8:414–23.
Yohe HC, Macala LJ, Giordano G, McMurray WJ (1992)Biochim Biophys Acta 1109:210–17.
Bartoszewicz Z, Koŝcielak J, Pacuszka T (1986)Carbohydr Res 151:77–88.
Nakamura K, Suzuki M, Taya C, Inagaki F, Yamakawa T, Suzuki A (1991)J Biochem 110:832–41.
Rokukawa C, Nakamura K, Handa S (1988)J Biochem 103:36–42.
Iwamori M, Sunada S, Ishihara E, Moki M, Fujimoto S, Nagai Y (1986)FEBS Lett 198:66–70.
Taki T, Hirabayashi Y, Ishikawa H, Ando S, Kon K, Tanaka Y, Matsumoto M (1986)J Biol Chem 261:3075–78.
Taki T, Ogura M, Nakajima M, Handa S (1993)Glycoconjugate J 10:273.
Kerbel RS, Twiddy RR, Robertson DM (1978)Int J Cancer 22:583–94.
Kerbel RS, Florian M, Man MS, Dennis J, McKenzie IFC (1980)J Natl Cancer Inst 64:1221–30.
Lehmann J, Vorlop J, Büntemeyer H (1988) InAnimal Cell Biotechnology (Spier RS, Griffiths JB, eds.) Vol. 3, pp. 221–37. New York: Academic Press.
Müthing J, Egge H, Kniep B, Mühlradt PF (1987)Eur J Biochem 163:407–16.
Momoi T, Ando S, Nagai Y (1976)Biochim Biophys Acta 441:488–97.
Ueno K, Ando S, Yu RK (1978)J Lipid Res 19:863–71.
Svennerholm L (1957)Biochim Biophys Acta 24:604–11.
Skipski VP (1975)Methods Enzymol 35:396–425.
Levery SB, Nudelman ED, Salyan MEK, Hakomori S (1989)Biochemistry 28:7772–81.
Karamanos NK, Wikström B, Antonopoulos CA, Hjerpe A (1990)J Chromatogr 503:421–29.
Unland F, Müthing J (1992)Biomed Chromatogr 6:155–59.
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957)J Biol Chem 226, 497–509.
Müthing J, Mühlradt PF (1988)Anal Biochem 173:10–17.
Magnani JL, Smith DF, Ginsburg V (1980)Anal Biochem 109:399–402.
Müthing J, Pörtner A, Jäger V (1992)Glycoconjugate J 9:265–73.
Wu G, Ledeen R (1988)Anal Biochem 173:368–75.
Young Jr. WW, MacDonald EMS, Nowinski RC, Hakomori S (1979)J Exp Med 150:1008–19.
Müthing J, Ziehr H (1990)Biomed Chromatogr 4:70–72.
Peter-Katalinić J, Egge H (1990)Methods Enzymol 193:713–33.
Ciucanu I, Kerek F (1984)Carbohydr Res 131:209–17.
Levery SB, Hakomori S (1987)Methods Enzymol 138E:13–25.
Hanisch FG, Peter-Katalinić J (1992)Eur J Biochem 205:527–35.
Williams MA, McCluer RH (1980)J Neurochem 35:266–69.
Nakamura K, Hashimoto Y, Suzuki M, Suzuki A, Yamakawa T (1984)J Biochem 96:949–57.
Nakamura K, Suzuki M, Inagaki F, Yamakawa T, Suzuki A (1987)J Biochem 101:825–35.
Müthing J, Schwinzer B, Peter-Katalinié J, Egge H, Mühlradt PF (1989)Biochemistry 28:2923–29.
Horikawa J, Yamasaki M, Iwamori M, Nakakuma H, Takatsuki K, Nagai Y (1991)Glycoconjugate J 8:354–60.
Ebel F, Schmitt E, Peter-Katalinić J, Kniep B, Mühlradt PF (1992)Biochemistry 31:12190–97.
Yohe HC, Cuny CL, Macala LJ, Saito M, McMurray W, Ryan JL (1991)J Immunol 146:1900–8.
Pörtner A, Peter-Katalinić J, Brade H, Unland F, Büntemeyer H, Müthing J (1993)Biochemistry 32:12685–93.
Hirabayashi Y, Hyogo A, Nakao T, Tsuchiya K, Suzuki Y, Matsumoto M, Kon K, Ando S (1990)J Biol Chem 265:8144–51.
Hashimoto Y, Suzuki A, Yamakawa T, Miyashita N, Moriwaki K (1983)J Biochem 94:2043–48.
Nagai Y, Nakaishi H, Sanai Y (1986)Chem Phys Lipids 42:91–103.
Ohsawa T, Nagai Y (1982)Exp Geront 17:287–93.
Ohsawa T (1989)Exp Geront 24:1–9.
Rösner H, Greis C, Rodemann HP (1990)Exp Cell Res 190:161–9.
Kawaguchi T, Takaoka T, Yoshida E, Iwamori M, Takatsuki K, Nagai Y (1988)Exp Cell Res 179:507–16.
Iber H, van Echten G, Klein RA, Sandhoff K (1990)Eur J Cell Biol 52:236–40.
Niimura Y, Ishizuka I (1990)Biochim Biophys Acta 1052:248–54.
Tsuchida T, Ravindranath MH, Saxton RE, Irie RF (1987)Cancer Res 47:1278–81.
Reuter G, Schauer R (1988)Glycoconjugate J 5:133–35.
IUPAC-IUB Commission on biochemical nomenclature (1977)Eur J Biochem 79:11–21.
Svennerholm L (1963)J Neurochem 10:613–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Abbreviations: FAB-MS, fast atom bombardment-mass spectrometry; GC-MS, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; GSL(s), glycosphingolipid(s); HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography; HPTLC, high performance thin layer chromatography; Neu5Ac,N-acetylneuraminic acid; Neu5Gc,N-glycoloylneuraminic acid [57]. The designation of the following glycosphingolipids follows the IUPAC-IUB recommendations [58] and the nomenclature of Svennerholm [59]. Gangliotriaosylceramide or GgOse3Cer, GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1Cer; gangliotetraosylceramide or GgOse4Cer, Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1Cer gangliopentaosylceramide or GgOse5Cer, GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1Cer; GM2, II3Neu5Ac-GgOse3Cer; GM1a, II3Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer; GM1b, IV3Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer; GalNAc-GM1b, IV3Neu5Ac-GgOse5Cer; GD1a, IV3Neu5Ac, II3Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer; GD1b, II3(Neu5Ac)2-GgOse4Cer; GD1α or GD1e, IV3Neu5Ac, III6Neu5AcGgOse4Cer; GD1e, IV3(Neu5Ac)2-GgOse4Cer; GT1b, IV3Neu5Ac, II3(Neu5Ac)2-GgOse4Cer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müthing, J., Peter-Katalinić, J., Hanisch, FG. et al. The ganglioside GD1α, IV3Neu5Ac, III6Neu5Ac-GgOse4Cer, is a major disialoganglioside in the highly metastatic murine lymphoreticular tumour cell line MDAY-D2. Glycoconjugate J 11, 153–162 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731155
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731155