Summary
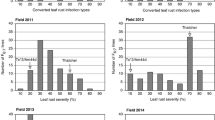
Ten wheat leaf rust (Puccinia recondita f.sp.tritici) race nurseries were planted in 1984. In five, each with a different race, no randomization of the 20 wheat genotypes was carried out. The remaining five race nurseries, also each with one of the same five races, were completely randomized. Comparison of the wheat genotype assesments was done using three procedures:
-
i)
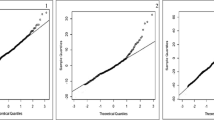
Correlating (Pearson's and Spearman's r) the leaf area affected of the twenty wheat genotypes in the randomized and the non-randomized nurseries;
-
ii)
comparing the best five wheat genotypes in each race nursery;
-
iii)
comparing the Wi-indeces of wheat genotypes in the randomized and non-randomized nurseries. All three procedures showed excellent agreement between the randomized and the non-randomized nurseries
. The use of a spreader row was most likely the reason for the large similarity. The consequence is that randomization is not sufficiently relevant to justify the increase in risk of mistakes and the extra administration needed. The host genotype-pathogen race interaction was significant and rather large. All but two genotype-race combinations showed a susceptible infection type, which indicates that partial resistance of wheat to wheat leaf rust caused the major part of this interaction. The results which suggest a gene-for-gene relationship, support the \lsintegrated concept\rs of Parlevliet and Zadoks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BennetE., 1973. Wheats of the Mediterranean Basin. In: O. H.Frankel (Ed.), Survey of crop genetic resources in their centres of diversity. FAO, Rome, p. 1–8.
HadjichristodoulouA. & A.Della, 1976. Genetic diversity in Cyprus. Plant genetic resources 32: 8–9.
LeeT. S. & G.Shaner, 1985a. Oligogenic inheritance of length of latent period in six slow leaf-rusting wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 75: 636–643.
LeeT. S. & G.Shaner, 1985b. Transgressive segregation of length of latent period in crosses between slow leaf-rusting wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 75: 643–647.
ParlevlietJ. E., 1975. Partial resistance of barley to leaf rust, Puccinia hordei I effect of cultivar and devellopment stage on latent period. Euphytica 24: 21–27.
ParlevlietJ. E. & A.vanOmmeren, 1984. Interplot interference and the assessment of barley cultivars for partial resistance to leaf rust,Puccinia hordei. Euphytica 33: 685–697.
ParlevlietJ. E. & J. C.Zadoks, 1977. The integrated concept of disease resistance; a new view including horizontal and vertical resistance in plants. Euphytica 26: 5–26.
PetersonR. F., A. B.Campbell & A. E.Hannah, 1948. A diagrammatic scale of estimating rust intensity on leaves and stems of cereals. Can. J. Res. C26: 496–500.
SnedecorG. W., 1980. Statistical methods. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, 507 pp.
WrickeG., 1962. Über eine Methode zur Erfassung der Ökologische Streubreite in Feldversuchen. Z. für Pflanzenzg. 47: 92–96.
WrickeG., 1964. Zur Berechnung der Ökovalenz bei Sommerweizen und Hafer. Z. fur Pllanzenzg 52: 127–138.
ZadoksJ. C., 1961. Yellow rust in wheat. Studies in epidemiology and physiological specialization. Tijdschr. Pl. Ziekten 67: 69–265.
Zadoks, J. C., 1963. The use of race nurseries in cereal resistance breeding in. In: Barley genetics I. Proc. 1st Int. Barley Genetics Symp. Pudoc, Wageningen, p. 242–249.
Zadoks, J. C., 1972. Modern concepts of disease resistance in cereals. In:F. G. H. Lupton, G. Jenkins & R. Johnson (Eds), The way ahead in plant breeding, Proc 6th Congr Eucarpia, P.B.I., Cambridge, p. 89–98.
ZadoksJ. C. & R. D.Schein, 1979. Epidemiology and plant disease managment. Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 427 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broers, L.H.M. Relevance of randomizing host genotypes of wheat that are tested for leaf rust resistance in race nurseries. Euphytica 36, 257–263 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730672
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730672