Conclusions
-
1.
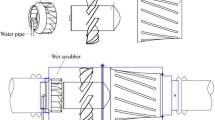
For wet removal of solid coke or catalyst particles it is recommended to use a scrubber with recoil plates consisting of sloped plane platforms, two-ramp recoil elements, or alternating hollow straight and tilted (truncated) cones.
-
2.
The “free” cross-sectional areas of the apertures in the bubbler mounted in the scrubber should constitute about 0.085% of the total cross-sectional area of the scrubber. It is recommended to direct the apertures upwards. The velocity of the steam in the apertures should be at least 20 m/sec.
-
3.
The area of the apertures in the perforated bucket mounted in the exhaust line should equal the cross-sectional area of the exhaust line, if open buckets are used and should be 3–4 times larger if closed buckets are used. The aperture diameter should measure 10–16 mm. It is recommended to provide the sedimentation tanks with bottoms sloped at angle of 60‡.
-
4.
The parameter values recommended for scrubbers are: slope of the plate 7‡, irrigation rate of the plate not lower than 1.1 m3/m2·h, rate of overflow over the plate rims not lower than 2–3 m3/m2·h.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 8, pp. 37–40, August, 1968.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soskind, D.M., Botnikov, Y.A., Barsukov, E.Y. et al. Scrubbers suitable for wet removal of dust. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 4, 600–604 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717721
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717721