Conclusions
-
1.
The range of Ms-Md is considerably narrower for athermal than for isothermal alloys. In connection with this, deformation at a temperature equidistant from Ms may lead to formation of much smaller quantities of martensite in athermal alloys.
-
2.
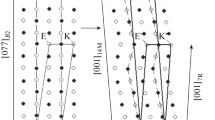
In athermal alloys (N30, N31) the structure of the strain martensite varies with the deformation temperature. Near Ms the strain martensite is similar to martensite formed during cooling. With increasing temperatures the martensite formed is of another morphological type, similar to isothermal martensite.
-
3.
In alloys N28, N29, N30, and N31 with phase strain hardened austenite the formation of martensite is accelerated considerably at small deformations (1–5%). At the same time, Md and the completeness of the transformation change negligibly.
-
4.
After phase strain hardening of athermal alloys the anomalous drop of the proof stress near Ms is retained. Phase strain hardening induces this effect in isothermal alloy N28.
-
5.
In the process of deformation at temperatures ensuring the optimal rate of martensite formation (40–50% martensite up until fracture) the ductility of both quenched and phase strain hardened austenite increases considerably.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. V. Nemirovskii, ,“Martensitic transformation in Fe−Ni alloys with compositions near that where the transformation mechanism changes,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,25, No. 5, 900 (1968).
V. N. Zambrzhitskii, O. P. Maksimova, and I. F. Moskvichev, ,“Martensitic transformation during deformation of athermal and isothermal Fe−Ni−C alloys,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,202, No. 6, 1304 (1972).
M. M. Shteinberg, D. A. Mirzaev, and L. G. Zhuravlev, ,“Characteristics of the martensitic transformation in iron and its alloys,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 9, 21 (1972).
Maki Tadashi et al., J. Japan Inst. Metals,35, No. 11, 1073 (1971).
Additional information
Chelyabinsk Polytechnic Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 11–14, June, 1977.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Povolotskii, V.D., Zhuravlev, L.G. & Shteinberg, M.M. Martensitic transformation during deformation of Fe−Ni alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 19, 434–438 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713077
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713077