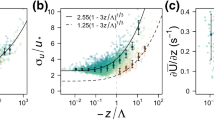
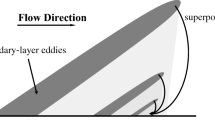
Abstract
During the last two decades, different scalings for convective boundary layer (CBL) turbulence have been proposed. For the shear-free regime, Deardorff (1970) introduced convective velocity and temperature scales based on the surface potential temperature flux,Q s , the buoyancy parameter, β, and the time-dependent boundary-layer depth,h. Wyngaard (1983) has proposed decomposition of turbulence into two components, bottom-up (b) and top-down (t), the former characterized byQ s , the latter, by the potential temperature flux due to entrainment,Q h . Sorbjan (1988) has devised height-dependent velocity and temperature scales for both b- and t-components of turbulence.
Incorporating velocity shear, the well known similarity theory of Monin and Obukhov (1954) has been developed for the atmospheric surface layer. Zilitinkevich (1971, 1973) and Betchov and Yaglom (1971) have elaborated this theory with the aid of directional dimensional analysis for a particular case when different statistical moments of turbulence can be alternatively attributed as being of either convective or mechanical origin.
In the present paper, we attempt to create a bridge between the two approaches pointed out above. A new scaling is proposed on the basis of, first, decomposition of statistical moments of turbulence into convective (c), mechanical (m) and covariance (c&m) contributions using directional dimensional analysis and, second, decomposition of these contributions into bottom-up and top-down components using height-dependent velocity and temperature scales. In addition to the statistical problem, the scaling suggests a new approach of determination of mean temperature and velocity profiles with the aid of the budget equations for the mean square fluctuations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATL:
-
alternative turbulence layer
- CBL:
-
convective boundary layer
- CML:
-
convective and mechanical layer
- FCL:
-
free convection layer
- MTL:
-
mechanical turbulence layer
References
Adrian, R. J., Ferreira, R. T. D. S., and Boberg, T.: 1986, ‘Turbulent Thermal Convection in a Wide Horizontal Fluid Layer’,Exp. Fluids 4, 121–141.
Berkowicz, R., and Prahm, L. P.: 1979, ‘Generalization of K-theory for Turbulent Diffusion. Part 1: Spectral Turbulent Diffusivity Concept’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 18, 266–272.
Berkowicz, R., and Prahm, L. P.: 1984, ‘Spectral Representation of the Vertical Structure of Turbulence in the Convective Boundary Layer’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 110, 35–52.
Betchov, R., and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971, ‘Comments on the Theory of Similarity as Applied to Turbulence in an Unstably Stratified Fluid’,Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Fiz. Atmosf. i Okeana 7, 1270–1279.
Blackadar, A. K.: 1962, ‘The Vertical Distribution of Wind and Turbulent Exchange in Neutral Atmosphere’,J. Geophys. Res. 67, 3095–3102.
Businger, J. A., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Bradley, F. F.: 1971, ‘Flux-Profile Relationships in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 181–189.
Caughey, S. J.: 1982, ‘Observed Characteristics of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. Van Dop (eds.),Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 107–158.
Coleman, G. N., Ferzinger, J. H. and Spalart, P. R.: 1990, ‘A Numerical Study of the Stratified Turbulent Ekman Layer’, Rept. No. TF-48, Thermosciences Division, Dept of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1970, ‘Convective Velocity and Temperature Scales for the Unstable Planetary Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 27, 1211–1213.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1972, ‘Numerical Investigation of Neutral and Unstable Planetary Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 29, 91–115.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1974, ‘Three-Dimensional Numerical Study of the Height and Mean Structure of a Heated Planetary Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 81–106.
Deardorff, J. W., and Willis, G. E.: 1985, ‘Further Results from a Laboratory Model of the Convective Planetary Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 32, 205–236.
Fiedler, B. H.: ‘An Integral Closure Model for the Vertical Turbulent Flux of a scalar in a Mixed Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 674–680.
Holtslag, A. A. M., and Moeng, C.-H.: 1991, ‘Eddy Diffusivity and Countergradient Transport in the Convective Atmospheric Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 1690–1698.
Holton, J. R.: 1992,An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Academic Press, San Diego, 507 pp.
Hunt, J. C. R.: 1984, ‘Turbulence Structure in Thermal Convection and Shear-Free Boundary Layers’,J. Fluid Mech. 138, 161–184.
Hunt, J. C. R., Kaimal, J. C., and Gaynor, J. E.: 1988, ‘Eddy Structure in the Convective Boundary Layer — New Measurements and New Concepts’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114, 827–858.
Kader, B. A., and Yaglom, A. M.: 1990, ‘Mean Fields and Fluctuation Moments in Unstably Stratified Turbulent Boundary Layers’,J. Fluid Mech. 212, 637–662.
Lenschow, D. H., Li, X. S., Zhu, C. J., and Stankov, B. B.: 1988, ‘The Stably Stratified Boundary Layer over the Great Plains’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 95–121.
Lenschow, D. H., and Stephens, P. L.: 1980, ‘The Role of Thermals in the Convective Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 19, 509–532.
Lykossov, V. N.: 1992, ‘The Momentum Turbulent Counter-Gradient Transport in Jet-Like Flows’,Adv. Atmos. Sci. 9, 191–200.
Mason, P. J.: 1992, ‘Large-Eddy Simulation of Dissipation in Convective Boundary Layers with Wind Shear’,Atmos. Environment 26A, 1561–1571.
Melgarejo, J. W., and Deardorff, J. W.: 1974, ‘Stability Functions for the Boundary-Layer Resistance Law Based upon Observed Boundary-Layer Heights’,J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1324–1333.
Moeng, C.-H., and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1984, ‘Statistics of Conservative Scalars in the Convective Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 3161–3169.
Moeng, C.-H., and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1989, ‘Evaluation of Turbulent Transport and Dissipation Closures in Second-Order Modeling’,J. Atmos. Sci. 46, 2311–2330.
Monin, A. S., and Obukhov, A. M.: 1954, ‘Basic Laws of Turbulent Mixing in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’,Trudy Geofiz. Inst. Adad. Nauk SSSR No 24 (151), 163–187.
Monin, A. S., and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971,Statistical Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 1, MIT Press, Cambridge MA, 769 pp.
Nieuwstadt, F. T. M.: 1984, ‘The Turbulent Structure of the Stable, Nocturnal Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 2202–2216.
Nieuwstadt, F. T. M., Mason, P. J., Moeng, C.-H., and Schumann, U.: 1993, ‘Large-Eddy Simulation of the Convective Boundary Layer: a Comparison of Four Computer Codes’, in F. Durst, R. Friedrich, F. W. Schmidt, U. Schumann and J. H. Whitelaw (eds.),Turbulent Shear Flows 8, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 343–367.
Obukhov, A. M.: 1946, ‘Turbulence in Thermally Nonhomogeneous Atmosphere’,Trudy Inst. Teor. Geofiz. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1, 95–115.
Obukhov, A. M.: 1960, “On the Structure of the Temperature and Velocity Fields in the Conditons of Free Convection’,Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geofiz. No. 9, 1392–1396.
Prandtl, L.: 1932, ‘Meteorologische Anwendungen der Strömungslehre’,Beitr. Phys. fr. Atmos. 19, 188–202.
Priestley, C. H. B.: 1955, ‘Free and Forced Convection in the Atmosphere Near the Ground’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 139–143.
Schmidt, H., and Schumann, U.: 1989, ‘Coherent Structure of the Convective Boundary Layer Derived from Large-Eddy Simulations’,J. Fluid Mech. 200, 511–562.
Schumann, U.: 1988, ‘Minimum Friction Velocity and Heat Transfer in the Rough Surface Layer of a Convective Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 44, 311–326.
Schumann, U.: 1993, Private communication.
Sorbjan, Z.: 1988, ‘Local Similarity in the Convective Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 45, 237–250.
Sorbjan, Z.: 1989,Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs NJ, 317 pp.
Sorbjan, Z.: 1990, ‘Similarity Scales and Universal Profiles of Statistical Moments in the Convective Boundary Layers’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 29, 762–775.
Sorbjan, Z.: 1991, ‘Evaluation of Local Similarity Functions in the Convective Boundary Layer’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 30, 1565–1583.
Sorbjan, Z., and Zilitinkevich, S.: 1993, ‘Towards Parameterization of the Convective Boundary Layer’, Unpublished manuscript.
Stull, R.: 1984, ‘Transilient Turbulence Theory. Part 1: The Concept of Eddy-Mixing Across Finite Distances’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 3351–3367.
Stull, R.: 1988,An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 666 pp.
Sykes, R. I., and Henn, D. S.: 1989, ‘Large-Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Sheared Convection’,J. Atmos. Sci. 46, 1106–1118.
Townsend, A. A.: 1961, ‘Equilibrium Layers and Wall Turbulence’,J. Fluid Mech. 11, 97–120.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1973, ‘On Surface Layer Turbulence, in D. A. Haugen (ed.),Workshop on Micrometeorology, American Meteorological Society, 101–149.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1983, ‘Lectures on the Planetary Boundary Layer’, in D. K. Lilly and T. Gal-Chen (eds.),Mesoscale Meteorology-Theories, Observations and Models, Reidel, Dordrecht, 603–650.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1987, ‘A Physical Mechanism for the Asymmetry in Top-Down and Bottom-Up Diffusion’,J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 1083–1087.
Wyngaard, J. C., and Brost, R. A.: 1984, ‘Top-Down and Bottom-Up Diffusion of a Scalar in Convective Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 102–112.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1971, ‘On Turbulence and Diffusion in Free Convection’,Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Fiz. Atmosf. i Okeana 7, 1263–1269.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1972, ‘On the Determination of the Height of the Ekman Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 141–145.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1973, ‘Shear Convection’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 416–423.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1975, ‘Resistance Laws and Prediction Equations for the Depth of the Planetary Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 741–752.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1991,Turbulent Penetrative Convection, Avebury Technical, Aldershot, 179 pp.
Zilitinkevich, S. S., and Deardorff, J. W.: 1974, ‘Similarity Theory for the Planetary Boundary Layer of Time-Dependent Height’,J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1449–1451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zilitinkevich, S. A generalized scaling for convective shear flows. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 70, 51–78 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712523
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712523