Summary
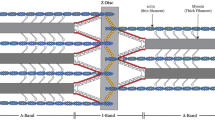
Synchrotron radiation was used for low-angle X-ray diffraction to monitor structural changes produced in insect flight muscle during fixation, dehydration and embedding for electron microscopy of thin sections. Fibre bundles were fixed by cold glutaraldehyde in one of three states, namely rigor, ATP or AMPPNP, followed by additional cross-linking treatment. No heavy metals were used before embedding. During fixation-embedding, all specimens lost the continuous actin layer lines of spacing 11–5 nm, shrank 18–21% in lattice spacing, shrank 0.5–2.5% in axial spacings and showed equatorial intensity changes which were similar for all three states, while the well-sampled inner layer lines (39–13 nm) were preserved with different fidelity in each state, highest for rigor and lowest for ATP. In different AMPPNP bundles, these layer lines indicated different degrees of unexplained shift (from slight to total) towards the structure of muscle fixed in ATP. Fixation in ATP caused obvious gain of intensity on 39, 19 and 13 nm layer lines, which can be interpreted as trapping of myosin crossbridge attachments to actin; this artifact was unchanged by seven variations in fixation conditions. Fixation in rigor gave no indication of crossbridge detachment nor of the presence or alteration of any significant population of non-bridging myosin heads. X-ray monitoring allowed selection of best-preserved samples for subsequent electron microscopy. The rapid pattern-recording possible with synchrotron X-ray intensity allowed us to complete and compare experiments with many fibre bundles from a single glycerinatedLethocerus muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BARRINGTON LEIGH, J., GOODY, R. S., HOFMANN, W., HOLMES, K. C., ROSENBAUM, G. & TREGEAR, R. T. (1977) The interpretation of X-ray diffraction from glycerinated flight muscle fibre bundles: new theoretical and experimental approaches. InInsect Flight Muscle (edited by TREGEAR, R. T.), pp. 137–164. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
BARRINGTON LEIGH, J. & ROSENBAUM, G. (1976) Synchrotron X-ray sources: A new tool in biological structural and kinetic analysis.Ann. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 5, 239–70.
BEINBRECH, G., KUHN, H. J. & RUEGG, J. C. (1972) Electron microscope and optical diffraction studies on glycerol-extracted insect flight muscle fibres relaxed by pyrophosphate.Experientia 28, 511–3.
BEINBRECH, G., KUHN, H. J., HERZIG, J. W. & RUEGG, J. C. (1976) Evidence for two attached myosin cross-bridge states of different potential energy.Cytobiologie 12, 385–96.
CHALOVICH, J. M., CHOCK, P. B. & EISENBERG, E. (1981) Mechanism of action of troponin-tropomyosin. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity without inhibition of myosin binding to actin.J. biol. Chem. 256, 575–8.
DONNAY, J. D. H. & DONNAY, G. (1967) Crystal geometry. InInternational Tables for X-ray Crystallography (edited by KASPER, J. S. & LONSDALE, K.), Vol. 2, p. 112.
GABRIEL, A. (1977) Position sensitive X-ray detector.Rev. Sci. Instrum. 48, 1303–5.
GIBBONS, I. R. (1975) The molecular basis of flagellar motility in sea urchin spermatozoa. InMolecules and Cell Movement (edited by INOUÉ, S. and STEPHENS, R. E.), pp. 207–232. New York: Raven Press.
GONZALES, F. (1962) A masking technique for contrast control in electron micrographs.J. Cell Biol. 15, 146–50.
GOODY, R. S., BARRINGTON LEIGHT, J., MANNHERZ, H. G., TREGEAR, R. T. & ROSENBAUM, G. (1976) X-ray titration of binding of beta, gamma-imido-ATP to myosin in insect flight muscle.Nature 262, 613–5.
GOODY, R. S., HOLMES, K. C., MANNHERZ, H. G., BARRINGTON LEIGH, J. & ROSENBAUM, G. (1975) Cross-bridge conformation as revealed by X-ray diffraction studies of insect flight muscle with ATP analogues.Biophys. J. 15, 687–705.
HOLMES, K. C., TREGEAR, R. T. & BARRINGTON LEIGH, J. (1980) Interpretation of the low angle X-ray diffraction from insect muscle in rigor.Proc. R. Soc. 207, 13–33.
LOVELL, S. J., KNIGHT, P. J. & HARRINGTON, W. H. (1981) Fraction of myosin heads bound to thin filaments in rigor fibrils from insect flight and vertebrate muscles.Nature 293, 664–6.
LEHRER, S. S. (1981) Damage to actin filaments by glutaraldehyde: protection by tropomyosin.J. Cell Biol. 90, 459–66.
MARSTON, S. B., RODGER, D. D. & TREGEAR, R. T. (1976) Changes in muscle crossbridges when beta, gamma-imido-ATP binds to myosin.J. molec. Biol. 104, 263–74.
MARSTON, S. B., TREGEAR, R. T., RODGER, C. D. & CLARKE, M. L. (1979) Coupling between the enzymatic site of myosin and the mechanical output of muscle.J. molec. Biol. 128, 111–26.
MEANS, G. E. & FEENEY, R. E. (1971)Chemical Modification of Proteins. San Francisco: Holden-Day.
MILLER, A. & TREGEAR, R. T. (1972) The structure of insect fibrillar flight muscle in the presence and absence of ATP.J. molec. Biol. 70, 85–104.
OFFER, G., COUCH, J., O'BRIEN, E. & ELLIOTT, A. (1981) Arrangement of cross-bridges in insect flight muscle in rigor.J. molec. Biol. 151, 663–702.
PHILLIPS, F. C. (1971)Introduction to Crystallography, 4th edn, p. 88. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
REEDY, M. C., REEDY, M. K. & GOODY, R. S. (1983) Co-ordinated electron microscopy and X-ray studies of glycerinated insect flight muscle. II. Electron microscopy and image reconstruction of muscle fibres in rigor, in ATP and in AMPPNP.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 4, 55–81.
REEDY, M. K. (1967) Cross-bridges and periods in insect flight muscle.Am. Zool. 7, 465–81.
REEDY, M. K. (1968) Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. Screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice.J. molec. Biol. 31, 155.
REEDY, M. K. (1971) Electron microscope observations concerning the behaviour of the cross-bridge in striated muscle. InContractility of Muscle Cells and Related Processes (edited by PODOLSKY, R. J.), pp. 229–246. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
REEDY, M. K. (1976) Preservation of X-ray patterns from frog sartorius muscle prepared for electron microscopy.Biophys. J. 16, 126a.
REEDY, M. K., BAHR, G. F. & FISCHMAN, D. A. (1973) How many myosins per cross-bridge? I. flight muscle myofibrils from the blowfly,Sarcophaga bullata.Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 37, 397–421.
REEDY, M. K. & BARKAS, A. E. (1974) Disordering of myofibril structure due to fixation, dehydration and embedding.J. Cell Biol. 63, 282a.
REEDY, M. K. & GARRETT, W. E. (1977) Electron microscope studies ofLethocerus flight muscle in rigor. InInsect Flight Muscle (edited by TREGEAR, R. T.), pp. 115–136. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
REEDY, M. K., HOLMES, K. C. & TREGEAR, R. T. (1965) Induced changes in orientation of the cross-bridges of glycerinated insect flight muscle.Nature 207, 1276.
REEDY, M. K., LEONARD, K. R., FREEMAN, R. & ARAD, T. (1981) Thick filament mass determination by electron scattering measurements with the scanning transmission electron microscope.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 2, 45–64.
SJOSTROM, M. & SQUIRE, J. M. (1977) Fine structure of the A-band in cryosections. The structure of the A-band of human skeletal muscle fibres from ultra-thin cryosections negatively stained.J. molec. Biol. 109, 49–68.
SQUIRE, J. M. (1971) General model for the structure of all myosin-containing filaments.Nature 233, 475–62.
SQUIRE, J. M. (1972) General model of myosin filament structure. II. Myosin filaments and cross-bridge interactions in vertebrate striated and insect flight muscles.J. molec. Biol. 72, 125–38.
WILLIAMS, N. E. & LUFT, J. H. (1968) Use of a nitrogen mustard derivative in fixation for electron microscopy and observations on the ultrastructure ofTetrahymena.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 25, 271–92.
WRAY, J., VIBERT, P & COHEN, C. (1978) Actin filaments in muscle: pattern of myosin and tropomyosin/troponin attachments.J. molec. Biol. 124, 501–21.
YAGI, N. & MATSUBARA, I. (1977) The equatorial X-ray diffraction pattern of crustacean striated muscles.J. molec. Biol. 117, 797–803.
YOUNT, R. G., BABCOCK, D., BALLANTYNE, W. & OJALA, D. (1971a) Adenylyl imidodiphosphate, an adenosine triphosphate analog containing a P-N-P linkage.Biochemistry 10, 2484–9.
YOUNT, R. G., OJALA, D. & BABCOCK, D. (1971b) Interaction of P-N-P analogs of adenosine triphosphate with heavy meromyosin and actomyosin.Biochemistry 10, 2490–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reedy, M.K., Goody, R.S., Hofmann, W. et al. Co-ordinated electron microscopy and X-ray studies of glycerinated insect flight muscle. I. X-ray diffraction monitoring during preparation for electron microscopy of muscle fibres fixed in rigor, in ATP and in AMPPNP. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 4, 25–53 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711957
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711957