Summary
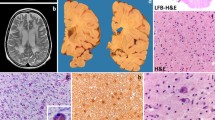
The progress and extent of myelination can be assessed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Myelination is delayed or diminished in several inherited metabolic abnormalities presenting in early life. Only minimal myelination of the CNS occurs in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Dysmyelination tends to produce fairly symmetrical lesions affecting white matter. In many mitochondrial enzyme and some lysosomal defects, the grey matter is also involved. The appearances and in particular the distribution on MRI and/or CT are characteristic in some conditions and the diagnosis is limited in others. Demyelination due to inflammatory disorders typically causes multifocal white matter lesions, recurrent in multiple sclerosis, monophasic in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, extending in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and classically involving the pons or corpus callosum in myelinolysis. Hypoxic ischaemic lesions may be metabolically induced and simulate primary demyelinating disorders. Mitochondrial enzyme defects in particular may present with stroke-like appearances. In many of these conditions, diagnosis is biochemical, but imaging has a significant role in suggesting the diagnosis, and documenting progression, response to therapy or complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown PE (1984) Molecular organisation of myelin. In Morell P, ed.Myelin, 2nd edn. New York: Plenum, 97–116.
Barkovich AJ, Jackson DE Jr (1989) MRI assessment of normal and abnormal brain myelination.MRI Divisions 19–25.
Brismar J, Harfi HA (1992) Partial albinism with immunodeficiency: a rare syndrome with prominent white matter changes.AJNR 13: 387–393.
Chang KH, Cha SH, Han MH, Park SH, Nah Dh, Hong JH (1992) Marchiafava-Bignami disease: serial changes in corpus callosum on MRI.Neuroradiology 34: 480–482.
Clifton A, Kendall BE, Kingsley DPE, Cross JH, Andar U (1991) Computed tomography in Alexander's disease: An atypical case with extensive low density in both frontal lobes.Neuroradiology 33: 438–440.
Demaerel Ph, Kendall BE, Kingsley D (1992) Cranial CT and MRI in diseases with DNA repair defects.Neuroradiology 34: 117–121.
Fukumizu M, Yoshikawa H, Takashima S, Sakuragawa N, Kurokawa T (1992) Tay-Sachs disease: progression of changes on neuroimaging in four cases.Neuroradiology 34: 483–496.
Kendall BE (1992) Disorders of lysosomes, peroxisomes, and mitochondria.AJNR 13: 621–653.
Kesselring J, Miller DH, Robb SA et al (1990)Brain 113: 291–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kendall, B.E. Inborn errors and demyelination: MRI and the diagnosis of white matter disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 16, 771–786 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711909
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711909