Summary
-
1.
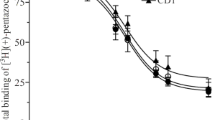
Naloxazone, a hydrazone derivative of naloxone which blocks mouse brain opiate receptorsin vivo for over 24 hr, produced a prolonged blockade of opiate receptor binding to rat brain membranesin vitro. At low concentrations (1-100 nM), naloxazone reversibly displaced [3H]naloxone binding. Incubation of brain homogenatesin vitro with 1-10µM naloxazone resulted in a loss of 40–60% of specific [3H]naloxone binding after four cycles of extensive washing or after extensive dialysis which removed 100% of similar concentrations of naloxone.
-
2.
Treatment with 5µM naloxazone also blocked binding of several3H-labeled opiate agonists and agonist-antagonists with no effect on muscarinic cholinergic orβ-adrenergic binding. Scatchard analysis of3H-labeled opiate binding after naloxazone pretreatment revealed a selective loss of high-affinity binding sites with minimal effects on low-affinity binding.
-
3.
Low-affinity sites remaining after naloxazone treatment were regulated by GTP and sodium like high-affinity sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blume, A. J. (1978). Opiate binding to membrane preparations of neuroblastoma × glioma hybrid cells NG 108-15: Effects of ions and nucleotides.Life Sci. 221843–1852.
Bylund, D. B., and Snyder, S. H. (1976).β-Adrenergic receptor binding in membrane preparations from mammalian brain.Mol. Pharmacol. 12568–580.
Caruso, T. P., Takemori, A. E., Larson, D. L., and Portoghese, P. S. (1979). Chloroxymorphamine, an opioid receptor site-directed alkylating agent having narcotic agonist activity.Science 204316–318.
Chang, K.- J., and Cuatrecasas, P. (1979). Multiple opiate receptors: Enkephalins and morphine binds to receptors of different specificity.J. Biol. Chem. 2542610–2618.
Chang, K.- J., Cooper, B. R., Hazum, E., and Cuatrecasas, P. (1979). Multiple opiate receptors: Different regional distribution and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides.Mol. Pharmacol. 1691–104.
Childers, S. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1978). Guanine nucleotides differentiate agonist and antagonist interactions with opiate receptors.Life Sci. 23759–762.
Childers, S. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1980). Differential regulation of guanine nucleotides of opiate agonist and antagonist receptor interactions.J. Neurochem. 34583–593.
Childers, S. R., Creese, I., Snowman, A. M., and Snyder, S. H. (1979). Opiate receptor binding affected differentially by opiates and opioid peptides.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 5511–18.
Feldman, H. (1972). Mathematical theory of complex ligand-binding systems at equilibrium: Some methods for parameter fitting.Anal. Biochem. 48317–338.
Hahn, E. F., Carroll-Buatti, M., and Pasternak, G. W. (1982). Irreversible opiate agonists and antagonists: The 14 hydroxydihydromorphinone azines.J. Neurosci. 2572–576.
Hazum, E., Chang, K.-J., Cuatrecasas, P., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Naloxazone irreversibly inhibits the high affinity binding of [125I] D-ala2-D-leu5-enkephalin.Life Sci. 282973–2979.
Lord, J., Waterfield, A., Hughes, J., and Kosterlitz, H. W. (1977). Endogenous opioid peptides: Multiple agonists and receptors.Nature 267495–499.
Martin, W. R., Eades, C. G., Thompson, J. A., Huppler, R. A., and Gilbert, P. E. (1976). The effects of morphine and nalorphine-like drugs in the non-dependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 197517–532.
Pasternak, G. W., and Hahn, E. F. (1980). Long-acting opiate agonists and antagonists: 14-Hydroxydihy-dromorphinones.J. Med. Chem. 23674–677.
Pasternak, G. W., and Snyder, S. H. (1975). Identification of novel high affinity opiate receptor binding in rat brain.Nature 253563–565.
Pasternak, G. W., Childers, S. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1980a). Opiate analgesia: Evidence for mediation by a subpopulation of opiate receptors.Science 208514–516.
Pasternak, G. W., Childers, S. W., and Snyder, S. H. (1980b). Naloxazone, a long-acting opiate antagonist: Effects on opiate receptor binding and analgesia in intact animals.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214455–462.
Pert, C. B., and Snyder, S. H. (1973). Opiate receptor: Demonstration in nervous tissue.Science 1791011–1014.
Pert, C. B., Pasternak, G. W., and Snyder, S. H. (1973). Opiate agonists and antagonists discriminated by receptor binding in brain.Science 1821359–1361.
Portoghese, P. S., Larson, D. L., Liang, J. B., Takemori, A. E., and Caruso, T. P. (1978). 6 Beta-[N-N-bis(2-chlorethyl)amino]-17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5-epoxy-3, 14-dihydroxymorphinan (Chlor-naltrexamine), a potent opioid receptor alkylating agent with ultralong narcotic antagonist activity.J. Med. Chem. 21589–599.
Schultz, R., Faase, E., Wuster, M., and Herg, A. (1979). Selective receptors for beta-endorphin on the rat vas deferens.Life Sci. 24843–850.
Simon, E. J., Hiller, J. M., and Edelman, I. (1973). Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic3H-etorphine to rat brain homogenate.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 701947–1949.
Simon, E. J., Hiller, J. M., Groth, J., and Edelman, I. (1975). Further properties of stereospecific opiate binding sites in rat brain: On the nature of the sodium effect.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 192531–537.
Terenius, L. (1973). Characteristics of the “receptor” for narcotic analgesics in synaptic plasma membrane fraction from rat brain.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 32377–384.
Wolozin, B. L., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 786181–6185.
Yamamura, H. I., and Snyder, S. H. (1974). Muscarinic cholinergic binding in rat brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 711725–1728.
Zhang, A.- Z., and Pasternak, G. W. (1980). Mu and delta receptors: Correlation with high and low affinity opiate binding sites.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 67323–324.
Zhang, A.- Z., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Opiates and enkephalins: A common binding site mediates their analgesic actions in rats.Life Sci. 29843–851.
Zhang, A.- Z., Chang, J. K., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). The actions of naloxazone on the binding and analgesic properties of morphiceptin (NH2Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-CONH2), a selective mu receptor ligand.Life Sci 282829–2836.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Childers, S.R., Pasternak, G.W. Naloxazone, a novel opiate antagonist: Irreversible blockade of rat brain opiate receptorsin vitro . Cell Mol Neurobiol 2, 93–103 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711075
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711075