Abstract
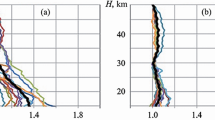
The nocturnal structure of the lower troposphere is studied using aerosol profile data (50–2800 m AGL) obtained with a bistatic, continuous wave, Argon ion lidar system during October 1986–September 1989 at Pune (18°32′ N, 73°51′ E, 559m AMSL), India. The top of the nocturnal groundbased inversion is taken as the height above ground where the negative vertical gradient in aerosol concentration first reaches a maximum. During the post-sunset period over this station, this height is as low as 160m and frequently lies around 550m. Greater heights are observed in pre-monsoon months and smaller ones during the southwest monsoon season. Positive vertical gradients in aerosol concentration, indicative of stable/elevated layers, appear frequently around 750m. Temporal variations of aerosol concentration gradients in two adjacent air layers, 920–1000m and 100–1100m, provide evidence that stability increases downward in the early night hours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, J. C. and Mahrt, L.: 1982, ‘The Nocturnal Surface Inversion and Influence of Clear-Air Radiative Cooling’,J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 864–878.
Devara, P. C. S. and Ernest Raj, P.: 1987, ‘A Bistatic Lidar for Aerosol Studies’,IETE Tech. Rev. 4, 412–415.
Devara, P. C. S. and Ernest Raj, P.: 1991, ‘Study of Atmospheric Aerosols in a Terrain-Induced Nocturnal Boundary Layer Using a Bistatic Lidar’,Atmos. Environ.25A, 655–660.
Devara, P. C. S., Raj. P. E., Murthy, B. S., Pandithurai, G., Sharma, S. and Vernekar, K. G.: 1992, ‘Comparison Between Lidar-Sodar Observations of Nocturnal Lower Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics over Pune’,Proc. National Space Science Symposium 1992, Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, India, March 11–14, 1992, pp. 449–450.
Endlich, R. M., Ludwig, F. L. and Uthe, E. E.: 1979, ‘An Automated Method for Determining the Mixing Depth from Lidar Observations’,Atmos. Environ. 13, 1051–1056.
Ernest Raj, P. and Devara, P. C. S.: 1989, ‘Some Results of Lidar Aerosol Measurements and Their Relationship with Meteorological Parameters’,Atmos. Environ. 23, 831–838.
Li Xing-sheng, Gaynor, J. E. and Kaimal, J. C.: 1983 ‘A Study of Multiple Stable Layers in the Nocturnal Lower Atmosphere’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 26, 157–168.
MacKinnon, D. J.: 1969, ‘The Effect of Hygroscopic Particles on the Backscattered Power from a Laser Beam’,J. Atmos. Sci. 26, 500–510.
Reiter, R., Carnuth, W. and Sladkovic, R.: 1968, ‘Effects of Atmospheric Fine Structure Characteristics on the Vertical Distribution of Aerosols’,Arch. Met. Geophy. Biokl., Ser. A. 17, 336–365.
Reiter, R. and Sladkovic, R.: 1970, ‘Control and Vertical Transport of Aerosol Between 700 and 3000m by the Lapse Rate and Fine Structure of Temperature: Results of a Sequence of Measurements Covering Several Years’,J Geophys. Res. 75, 3065–3075.
Russell, P. B. and Uthe, E. E.: 1978a, ‘Regional Patterns of Mixing Depths and Stability: Sodar Network Measurements for Input to Air Quality Models’,Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 59, 1275–1287.
Russell, P. B. and Uthe, E. E.: 1978b, ‘Acoustic and Direct-Measurements of Atmospheric Mixing at Three Sites During an Air Pollution Incident’,Atmos. Environ. 12, 1061–1074.
Sasano, Y., Shigematsu, A., Shimizu, H., Takeuchi, N. and Okuda, M.: 1982, ‘On the Relationship Between the Aerosol Layer Height and the Mixed Layer Height Determined by Laser Radar and Low-level Radiosonde Observations’,J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 60, 889–895.
Sasano, Y., Matsui, I., Shimizu, H. and Takeuchi, N.: 1983, ‘Automatic Determination of Atmospheric Mixed Layer Height in Routine Measurements by a Laser Radar’,J. Japan Soc. Air Pollut. 18, 175–183.
Singal, S. P.: 1989, ‘Acoustic Sounding Stability Studies’, inEncyclopedia of Environmental Control Technology, Gulf Publishing Co., London, pp. 1003–1061 (P. N. Cheremisinoff, editor).
Tombach, I, and Chan, M.: 1976, ‘Estimation of Mixing Depth and Inversion Height by Acoustic Radar—A Comparison with In-situ Measurements’,Proc. 17th Conf. Radar Meteorlogy, American Meteorological Society, Seattle, Washington, Oct. 26–29, 1976, pp. 313–320.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, P.E., Devara, P.C.S. On the stable stratification of the nocturnal lower troposphere inferred from lidar observations over Pune, India. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 65, 197–205 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00708824
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00708824