Summary
-
1.
The O2 consumption and aerobic lactate production of porcine carotid artery have been studied in relation to active isometric tension maintenance in order to estimate the tension cost, i.e., ATP hydrolysis rate per unit force maintained.
-
2.
The relationship between total metabolism and isometric force was measured at several muscle lengths in order to distinguish tension-dependent and-independent components of ATP utilization.
-
3.
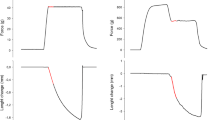
At the maximum isometric tension observed, 2 kg wt/cm2, 1.3 μmole ATP/min per gram wet weight out of a total metabolism of 2 μmole/min is tension dependent.
-
4.
The absolute levels of force, O2 consumption, lactate production and the ratio of oxidative to glycolytic metabolism varied considerably with the stimulant; however, the tension-dependent ATP utilization was invariant with respect to the mode of stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, F. T., Somlyo, A. V., Somlyo, A. P.: The contractile apparatus of vascular smooth muscle: Intermediate high voltage stereo electron microscopy. J. molec. Biol.98, 17–29 (1975)
Beviz, A. L., Lundholm, L., Mohme-Lundholm, E.: Energy exchange in isometric contraction of vascular smooth muscle induced by K+ ions. Acta physiol. scand.76, 441–445 (1969)
Colquhoun, D.: Lectures on biostatistics, p. 103. London-Oxford: University Press 1974
Daemers-Lambert, C.: Action due clorure de potassium sur le metabolisme des esters phosphores et le tonus du muscle arteriel (carotide de bovide). Angiologica1, 249–274 (1964)
Daemers-Lambert, C.: Dissociation par le fluorodinitrobenzene des effets ATP-asiques, metabolique et contractile, lies a l'augmentation de la concentration et potassium extracellulaire, dans le muscle lisse arteriel (carotide de bovide). Angiologica5, 293–300 (1968)
Daemers-Lambert, C.: Action du fluordinitrobenzene sur le metabolisme phosphore du muscle lisse arteriel pendant la stimulation electrique (carotide de bovide). Angiologica6, 1–12 (1969)
Daemers-Lambert, C., Roland, J.: Metabolisme des esters phosphores pendant le developpement et le maintien de la tension phasique du muscle lisse arteriel (carotide de bovide). Angiologica4, 69–87 (1967)
Eccleston, J. F., Geeves, M. A., Trentham, D. R., Bagshaw, C. R., Mrwa, U.: The binding and cleavage of ATP in the myosin and actomyosin ATPase mechanisms. In: Molecular basis of motility (L. M. G. Heilmeyer, J. C. Rüegg, and T. Wieland, eds.), pp. 42–52. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Glück, E. V.: Aerober Stoffwechsel und Energieumsatz des Arterienmuskels in Abhängigkeit vom Kontraktionszustand. Inaugural-Dissertation, Medizinische Fakultät, Ruprecht-Karl-Universität, Heidelberg 1976
Herlihy, J. T., Murphy, R. A.: Length-tension relationship of smooth muscle of the hog carotid artery. Circulat. Res.33, 275–283 (1973)
Homsher, E., Mommaerts, W. F. H. M., Ricchiuti, N. V., Wallner, A.: Activation heat, activation metabolism and tension-related heat in frog semitendinosus muscles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)220, 601–625 (1972)
Knull, H. R., Bose, D.: Reversibility of mechanical and biomedical changes in smooth muscle due to anoxia and substrate depletion. Amer. J. Physiol.229, 329–333 (1975)
Kushmerick, M. J., Paul, R. J.: Aerobic recovery metabolism following a single isometric tetanus in frog sartorius muscle at 0°C. J. Physiol. (Lond.)254, 693–709 (1976)
Lundholm, L., Mohme-Lundholm, E.: Energetics of isometric and isotonic contraction in isolated vascular smooth muscle under anaerobic conditions. Acta physiol. scand.64, 275–282 (1965)
Lundholm, L., Mohme-Lundholm, E., Vamos, N.: Lactic acid assay withL(+)lactic acid dehydrogenase from rabbit muscle. Acta physiol. scand.58, 243–249 (1963)
Murphy, R. A., Herlihy, J. T., Megerman, J.: Force-generating capacity and contractile protein content of arterial smooth muscle. J. gen. Physiol.64, 691–705 (1974)
Needham, D. M.: The biochemistry of muscular contration in its historical development. In: Machina carnis, pp. 559–566. London: Cambridge University Press 1971
Needleman, P., Blehm, D. J.: Effect of epinephrine and potassium chloride on contraction and energy intermediates in rabbit thoracic aorta strips. Life Sci.9, 1181–1189 (1970)
Paul, R. J., Glück, E., Rüegg, J. C.: Cross bridge ATP utilization in arterial smooth muscle. Pflügers Arch.361, 297–299 (1976)
Paul, R. J., Peterson, J. W.: Relation between length, isometric force, and O2 consumption rate in vascular smooth muscle. Amer. J. Physiol.228, 915–922 (1975)
Paul, R. J., Peterson, J. W.: The mechanochemistry of smooth muscle. In: Biochemistry of smooth muscle (N. L. Stephens, ed.), pp. 15–39. Baltimore: University Park Press 1977
Paul, R. J., Peterson, J. W., Caplan, S. R.: Oxygen consumption rate in vascular smooth muscle: relation to isometric tension. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst)305, 474–480 (1973)
Paul, R. J., Peterson, J. W., Caplan, S. R.: A nonequilibrium thermodynamic description of vascular smooth muscle mechanochemistry. I. The rate of oxygen consumption: a measure of the driving chemical reaction. J. Mechanochem. Cell Moti.3, 19–32 (1974)
Paul, R. J., Rüegg, J. C.: Biochemistry of vascular smooth muscle: Energy metabolism and proteins of the contractile apparatus. In: Microcirculation II (B. M. Altura and G. Kaley, eds.). Baltimore: University Park Press 1977 (in press)
Peterson, J. W., Paul, R. J.: Aerobic glycolysis in vascular smooth muscle: relation to isometric tension. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)357, 167–176 (1974a)
Peterson, J. W., Paul, R. J.: Effects of initial length and active shortening on vascular smooth muscle contractility. Amer. J. Physiol.227, 1019–1024 (1974b)
Pittman, R. N., Duling, B. R.: Oxygen sensitivity of vascular smooth muscle. I. In vitro studies. Microvasc. Res.6, 202–211 (1973)
Rüegg, J. C.: Smooth muscle tone. Physiol. Rev.51, 201–248 (1971)
Sandberg, J. A., Carlson, F. D.: The length dependence of phosphorylcreatine hydrolysis during an isometric tetanus. Biochem. Z.345, 212–231 (1966)
Scott, R. F., Morrison, E. S., Kroms, M.: Effect of cold shock on respiration and glycolysis in swine arterial tissue. Amer. J. Physiol.219, 1363–1365 (1970)
Sparks, H. V., Bohr, D. F.: Effect of stretch on passive tension and contractility of isolated vascular smooth muscle. Amer. J. Physiol.202, 835–840 (1962)
Vallieres, J., Scarpa, A., Somlyo, A. F.: Subcellular fractions of smooth muscle. I. Isolation, substrate utilization and Ca2+ transport by main pulmonary artery and mesenteric vein mitochondria. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.170, 659–669 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glück, E., Paul, R.J. The aerobic metabolism of porcine carotid artery and its relationship to isometric force. Pflugers Arch. 370, 9–18 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707939
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707939