Summary
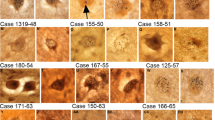
Combined Golgi/pigment studies revealed that pyramidal neurons and non-pyramidal cells of the Ammon's horn of the human adult can be distinguished from each other by their characteristic lipofuscin pigment deposits. In sector CA1, both the typical pyramidal neurons and the modified forms of pyramidal cells contain a modest amount of fine lipofuscin granules while non-pyramidal cells are either pigment-laden or devoid of lipofuscin deposits. Strips running through the whole depth of the pyramidal cell layer and the stratum oriens of CA1 were examined and all nucleolated nerve cells present within these strips were classified and counted (16 brains, age range from 28 to 69 years). Of the 18,510 neurons classified, 16,765 were pyramidal cells, including their modified versions, and 1,745 were non-pyramidal cells. The pyramidal cells, accordingly, were intermixed with 9.4±1.0% non-pyramidal neurons. The data presented provide a basis for investigation of the aging and diseased human brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P (1975) Organization of hippocampal neurons and their interconnections. In: Isaacson RL, Primbram KH (eds) The hippocampus. Vol. 1. Structure and development. Plenum press, New York, pp 155–175
Ball MJ (1977) Neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles and granulovacuolar degeneration in the hippocampus with aging and dementia — a quantitative study. Acta Neuropathol 37:111–118
Blackstad TW (1956) Commissural connections of the hippocampal region in the rat, with special reference to their mode of termination. J Comp Neurol 105:417–538
Backstad TW (1967) Cortical grey matter. A correlation of light and electron microscopic data. In: Hyden H (ed) The neuron. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 49–118
Braak H (1974) On the structure of the human archicortex. I. The cornu ammonis. A Golgi and pigmentarchitectonic study. Cell Tissue Res 152:349–383
Braak H (1980) Architectonics of the human telencephalic cortex. In: Braitenberg V, Barlow HB, Bizzi E, Florey E, Grüsser OJ, van der Loos H (eds) Studies of brain function, Vol 4. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–147
Braak H (1983) Transparent Golgi impregnations: a way to examine both details of cellular processes and components of the cell body. Stain Technol 58:91–95
Braak H (1984) Architectonics as seen by lipofuscin stains. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex. Plenum press, New York, pp 59–104
Braitenberg V, Schüz A (1983) Some anatomical comments on the hippocampus. In: Seifert W (ed) Neurobiology of the hippocampus. Academic press, New York, pp 21–37
Buzsáki G, Eidelberg E (1982) Direct afferent excitation and long term potentiation of hippocampal interneurons. J Neurophysiol 48:597–607
Cassell MD, Brown MW (1977) Cell counts for the stratum pyramidale of the hippocampus of the rat. Life Sci 21:1187–1191
Feldman ML (1984) Morphology of the neocortical pyramidal neuron. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex. Plenum press, New York, pp 123–200
Frotscher M, Léránth C, Lübbers K, Oertel WH (1984) Commissural afferents innervate glutamate decarboxylase immuno-reactive non-pyramidal neurons in the guinea pig hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 46:137–143
Knowles WD, Schwartzkroin PA (1981) Local circuit synaptic interactions in hippocampal brain slices. J Neurosci 1:318–322
Konigsmark BW (1970) Methods for the counting of neurons. In: Nauta WJH, Ebbesson SOE (eds) Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy. Springer, New York, pp 315–340
Lorente de Nó R (1934) Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the study of the ammonic system. J Psychol Neurol 46:113–177
Miller AKH, Alston RL, Mountjoy CQ, Corsellis JAN (1984) Automated differential cell counting on a sector of the normal human hippocampus: The influence of age. Neuropath Appl Neurobiol 10:123–141
Mouritzen Dam A (1979) The density of neurons in the human hippocampus. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 5:249–264
Niklowitz W, Bak IJ (1965) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Ammonshorn. I. Die normale Substruktur der Pyramidenzellen. Z Zellforsch 66:529–547
Ramón y Cajal S (1911) Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. Tome II. Maloine, Paris
Ribak CE, Vaughn JS, Saito K (1978) Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in neuronal somata following colchicine inhibition of axonal transport. Brain Res 140:315–332
Rose JE (1940) Zur normalen und pathologischen Architektonik der Ammonsformation. J Psychol Neurol 49:137–188
Sachs L (1979) Angewandte Statistik. Springer, Berlin
Schmechel DE, Vickrey BG, Fitzpatrick D, Elde RP (1984) GABAergic neurons of mammalian cerebral cortex: widespread subclass defined by somatostatin content. Neurosci Lett 47:227–232
Schwartzkroin PA, Kunkel DD (1985) Morphology of identified interneurons in the CA1 regions of guinea pig hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 232:205–218
Schwartzkroin PA, Mathers LH (1978) Physiological and morphological identification of a non-pyramidal hippocampal cell type. Brain Res 157:1–10
Smolen AJ, Wright LL, Cunningham TJ (1983) Neuron numbers in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion of the rat: A critical comparison of methods for cell counting. J Neurocytol 12:739–750
Somogyi P, Nunzi MG, Gorio A, Smith AD (1983) A new type of specific interneuron in the monkey hippocampus forming synapses exclusively with the axon initial segments of pyramidal cells. Brain Res 259:137–142
Somogyi P, Hodgson AJ, Smith AD, Nunzi MG, Gorio A, Wu JY (1984) Different populations of GABA-ergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci 4:2590–2603
Tömböl T, Somogyi G, Hajdu F (1978) Golgi study on cat hippocampal formation. Anat Embryol 15:331–350
Vogt C, Vogt O (1937) Sitz und Wesen der Krankheiten im Lichte der topistischen Hirnforschung und des Variierens der Tiere. J Psychol Neurol 47:237–457
Wall G (1972) Über die Anfärbung der Neurolipofuszine mit Aldehydfuchsinen. Histochemie 29:155–171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olbrich, HG., Braak, H. Ratio of pyramidal cells versus non-pyramidal cells in sector CA1 of the human Ammon's horn. Anat Embryol 173, 105–110 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707308
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707308