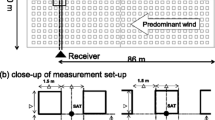
Abstract
Line-averaged measurements of the structure parameter of refractive index (C 2 n ) were made using a semiconductor laser diode scintillometer above two markedly different surfaces during hours of positive net radiation. The underlying vegetation comprised in the first instance a horizontally homogeneous, pasture sward well-supplied with water, and in the second experiment, a sparse thyme canopy in a semi-arid environment. Atmospheric stability ranged between near neutral and strongly unstable (−2≤ζ≤0). The temperature structure parameterC 2 T computed from the optical measurements over four decades from 0.001 to 2 K2 m−2/3 agreed to within 5% of those determined from temperature spectra in the inertial sub-range of frequencies. Spectra were obtained from a single fine thermocouple sensor positioned near the midway position of the 100m optical path and at the beam propagation height (1.5m).
With the inclusion of cup anemometer measurements, rule-of-thumb assumptions about surface roughness, and Monin-Obukhov similarity theory, path-averaged optical scintillations allow calculation of surface fluxes of sensible heat and momentum via a simple iterative procedure. Excellent agreement was obtained between these fluxes and those measured directly by eddy correlation. For sensible heat, agreement was on average close to perfect over a measured range of 0 to 500 W m−2 with a residual standard deviation of 30 W m−2. Friction velocities agreed within 2% over the range 0–0.9 m s−1 (residual standard deviation of 0.06 m s−1). The results markedly increase the range of validation obtained in previous field experiments. The potential of this scintillation technique and its theoretical foundation are briefly discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas, E. L.: 1989, ‘Two-Wavelength Method of Measuring Path-Averaged Turbulent Surface Heat Fluxes’,J. Atm. and Ocean. Techn. 7, 801–804.
Andreas, E. L. (ed.): 1990,Selected Papers on Turbulence in a Refractive Medium, SPIE Milestone Series, Vol. 25, Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers, Bellingham WA.
Coppin, P. A.: 1982, ‘An Examination of Cup Anemometer Overspeeding’,Meteorol. Rdsch. 35, 1–11.
Fairall, C. W., Edson, J. B., Larsen, S. E. and Mestayer, P. G.: 1990, ‘Inertial-Dissipation Air-Sea Flux Measurements: A Prototype System using Realtime Spectral Computations’,J. Atmos. and Ocean. Techn. 7, 425–453.
Green, A. E., Judd, M. J., McAneney, J. K., Astill, M. S. and Prendergast, P. T.: 1991, ‘A Rapid-Response 2-D Drag Anemometer for Atmospheric Turbulence Measurements’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 57, 1–15.
Hill, R. J.: 1978, ‘Models of the Scalar Spectrum for Turbulent Advection’,J. Fluid Mech. 88, 541–562.
Hill, R. J. and Clifford, S. F.: 1978, ‘Modified Spectrum of Atmospheric Turbulence Fluctuations and its Application to Optical Propagation’,J. Opt. Soc. Am. 68, 892–899.
Hill, R. J.: 1992, ‘Review of Optical Scintillation Methods of Measuring the Refractive-Index Spectrum, Inner Scale and Surface Fluxes’,Waves in Random Media 2, 179–201.
Hill, R. J., Ochs, G. R. and Wilson, J. J.: 1992, ‘Measuring Surface-Layer Fluxes of Heat and Momentum using Optical Scintillation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 391–408.
Højstrup, J.: 1981, ‘A Simple Model for the Adjustment of Velocity Spectra in Unstable Conditions Downstream of an Abrupt Change in Roughness and Heat Flux’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 341–356.
Hufnagel, R. E. and Stanley, N. R.: 1964, ‘Modulation Transfer Function Associated with Image Transmission through Turbulent Media’,J. Optical Soc. of America 54, 52–61.
Kaimal, J. C., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y. and Cote, O. R.: 0000, ‘Spectral Characteristics of Surface Layer Turbulence’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 653–689.
Kohsiek, W.: 1982, ‘MeasuringC 2 T ,C 2 Q andC TQ in the Unstable Surface Layer, and Relations to the Vertical Fluxes of Heat and Moisture’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 89–107.
Kohsiek, W. and Herben, M. H. A. J.: 1983, ‘Evaporation Derived from Optical and Radio-Wave Scintillation’,Applied Optics 22, 2566–2569.
Kohsiek, W.: 1985, ‘A Comparison between Line-Averaged Observation ofC 2 n from Scintillation of a CO2 Laser Beam and Time Averagedin situ Observations’,J. Climate and Appl. Meteorol. 24, 1099–1102.
Lagouarde and McAneney, K. J.: 1992, ‘Daily Sensible Heat Flux Estimation from a Single Measurement of Surface Temperature and Maximum Air Temperature’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 59, 341–362.
Priestley, C. H. B. and Taylor, R. J.: 1972, ‘On the Assessment of Surface Heat Flux and Evaporation Using Large Scale Parameters’,Mon. Weather Rev. 100, 81–92.
Panofsky, H. A. and Dutton, J. A.: 1984,Atmospheric Turbulence, Models and Methods for Engineering Applications, John Wiley & Sons, New York. 397 pp.
Ochs, G. R. and Cartwright, W. D.: 1980, ‘Optical System IV for Space-Averaged Wind andC 2 n Measurements’, NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL WPL-52, NOAA Environmental Research Laboratories, Boulder, CO, 31 pp.
Seguin, B., Assad, E., Imbernon, J. P., Kerr, Y., and Lagouarde, J. P.: 1989, ‘Use of Meteorological Satellites for Water Balance Monitoring in Sahelian Regions’,Int. J. Remote Sensing 10, 1101–1117.
Stanhill, G.: 1969, ‘A Simple Instrument for the Field Measurement of Turbulent Diffusion Flux’,J. Applied Meteorol. 8, 509–513.
Strohbehn, J. W.: 1968, ‘Line-of-Sight Wave Propagation through the Turbulent Atmosphere’,Proceedings of the IEEE 57, 703–704.
Tanner, C. B. and Pelton, W. L.: 1960, ‘Potential Evapotranspiration Estimates by the Approximate Energy Balance Method of Penman’,J. Geophys. Res. 65, 3391–3413.
Wang Ting-i, Ochs G. R. and Clifford S. F.: 1978, ‘A Saturation-Resistant Optical Scintillometer to MeasureC 2 n ’,J. Opt. Soc. Amer. 68, 334–338.
Tanner, B. D., Tanner, M. S., Dugas, W. A., Campbell, E. C. and Bland, B. L.: 1985, ‘Evaluation of an Operational Eddy Correlation System for Evapotranspiration Measurements’,National Conference o on Advances in Evapotranspiration American Society of Agricultural Engineers., Chicago, IL, December 16–17, 1985.
Tennekes, H. and Lumley, J. L.: 1972,A First Course in Turbulence, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass., 300 pp.
Thiermann, V. and Azoulay, E.: 1989, ‘Modelling of Structure Constant and Inner Scale of Refractive Index Fluctuations — an Experimental Investigation’,Proc. SPIE 1115, 124–135.
Thiermann, V. and Grassl, H.: 1992, ‘The Measurement of Turbulent Surface-Layer Fluxes by use of Bichromatic Scintillation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 367–389.
Theirmann, V.: 1992, ‘A Displaced-Beam Scintillometer for Line-Averaged Measurements of Surface Layer Turbulence’,Tenth Symposium on Turbulence and Diffusion, American Meteorological Society, Portland, Oregon, September 29–October 2, 1992.
Wesely, M. L.: 1976a, ‘A Comparison of Two Optical Methods for Measuring Line Averages of Thermal Exchanges Above Warm Surfaces’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 15, 1177–1188.
Weseley, M. L.: 1976b, ‘The Combined Effect of Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations on Refractive Index’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 15, 43–49.
Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y. and Collins, S. A.: 1971, ‘Behaviour of the Refractive Index Structure Parameter near the Ground’,J. Opt. Soc. Am. 61, 1626–1650.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Coté, O. R.: 1971, ‘The Budgets of Turbulent Kinetic Energy and Temperature Variance in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 190–201.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1973, ‘On Surface-Layer Turbulence’, pp. 101–149, in D. A. Haughen (ed.),Workshop on Micrometeorology, American Meteorological Society, Boston, Mass. 392 pp.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Clifford, S. F.: 1978, ‘Estimating Momentum, Heat and Moisture Fluxes from Structure Parameters’,J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 1204–1211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, A.E., McAneney, K.J. & Astill, M.S. Surface-layer scintillation measurements of daytime sensible heat and momentum fluxes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 68, 357–373 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00706796
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00706796