Abstract
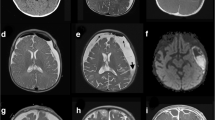
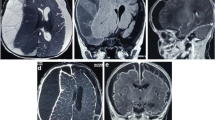
A case is reported of an infant with bilateral subdural empyema due toSalmonella enteritidis. ThisSalmonella species is extremely uncommon as a pathogen in a focal infection in the central nervous system. Treatment by early surgical drainage, followed by systemic antibiotics and subdural irrigation, was successful. This is the first case reported of infantile subdural empyema due toS. enteritidis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannister G, Williams B, Smith S (1981) Treatment of subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 55:82–88
Brzeziński J, Planeta-Malecka I, Zierski J, Bielinska W (1969) Cerebral abscess duringSalmonella enteritidis infection in an 8-month-old infant. Pediatr Pol 44:223–226 (in Polish)
Buchanan N, Berger H, Hoogstraten RCJ van (1973) Subdural empyema caused bysalmonella typhimurium. S Afr Med J 47:1345–1346
Enzmann DR (1984) Imaging of infections and inflammations of the central nervous system: computed tomography, ultrasound, and nuclear magnetic resonance. Raven Press, New York, pp 234–246
Fukuoka H, Takagi T, Mizuno S, Wakabayashi S, Nagai H, Ishikawa T, Nakanishi M (1983) Subdural empyema in children: a follow-up study of seven cases. No To Hattatsu (Tokyo) 15:310–316 (in Japanese)
Herbert DA, Ruskin J (1982)Salmonella typhi epidural abscess occurring 47 years after typhoid fever. Case report. J Neurosurg 57:719–721
Hockley AD, Williams B (1983) Surgical management of subdural empyema. Child's Brain 10:294–300
Kaufman DM, Miller MH, Steigbigel NH (1975) Subdural empyema: analysis of 17 recent cases and review of the literature. Medicine 54:485–498
Lerner PI, Golden PF, Jane JA (1972)Salmonella-infected subdural hematoma. Pediatrics 49:127–128
Moritaka K, Hayashi T, Shojima K, Honda E, Yamamoto M, Komatsu R, Tanaka C (1984) Clinical analysis of subdural empyema in children. Nerv Syst Child 9:215–222 (in Japanese)
Odeku EL, Ransome-Kuti O, Elam HP (1967) Aneurysm of great vein of Galen complicated by chronic subdural abscess. West Afr Med J 16:109–113
Paniker CKJ, George K (1965) Otogenic brain abscess caused bySalmonella typhimurium. J Indian Med Assoc 45:451–452
Saphra I, Winter JW (1957) Clinical manifestations of salmonellosis in man. An evaluation of 7779 human infections identified at the New York Salmonella Center. N Engl J Med 256:1128–1134
Smith HP, Hendrick B (1983) Subdural empyema and epidural abscess in children. J Neurosurg 58:392–397
Suzuki Y, Sugiyama Y, Ishii R, Sato I (1976) Brain abscess caused bySalmonella typhi. J Neurosurg 45:709–711
West SE, Goodkin R, Kaplan AM (1977) Neonatal salmonella meningitis complicated by cerebral abscesses. West J Med 127:142–145
Yamada H, Kida H, Hino T, Ando T, Sakai N (1980) Subdural empyema. Report of 9 cases and review of the literature in Japan. Neurol Surg (Tokyo) 8:539–544 (in Japanese)
Yoshikawa TT, Chow AW, Guze LB (1975) Role of anaerobic bacteria in subdural empyema: Report of four cases and review of 327 cases from English literature. Am J Med 58:99–104
Zimmermann RD, Leeds NE, Danziger A (1984) Subdural empyema: CT findings. Radiology 150:417–422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okudera, H., Toba, Y. & Kyoshima, K. Bilateral subdural empyema due toSalmonella enteritidis in an infant. Child's Nerv Syst 5, 45–46 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00706749
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00706749