Abstract
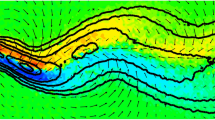
This paper describes an experimental investigation of the behaviour of the statistics of concentration fluctuations in a passive plume dispersing over a two-dimensional hill of moderate steepness. Recently developed high frequency response Flame Ionization Detector (FID) technology with a frequency response in excess of 200 Hz was utilized to obtain an extensive set of measurements of the mean and fluctuating plume concentrations. Plumes dispersing over flat terrain and over a hill with a maximum slope of 0.3 were studied. For both cases, extensive turbulent flow measurements were also carried out.
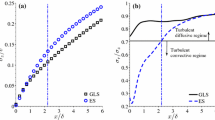
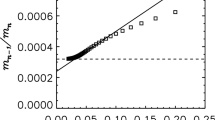
The measured mean plume concentration profiles were of a generally Gaussian form and showed the expected effects of surface reflection for the flat terrain and hill. Plume intermittency and concentration fluctuation intensity were calculated at all measurement locations. Conditional and unconditional plume concentration statistics were calculated. The conditional (in-plume) concentrations and intensities were more uniform with height than for the unconditional ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bluemen, W. (ed.): 1990, ‘Atmospheric Processes Over Complex Terrain’,Micrometeorological Monographs 23, 83–143.
Cambustion Ltd.: 1990, ‘HFR300 Fast FID User Manual and Specifications’, 1–11.
Carruthers, D. J., Hunt, J. C. R. and Holroyd, R. J.: 1989, ‘Airflow and Dispersion Over Complex Terrain’,Air Pollution Modelling and its Application VII, Plenum, 515–529.
Dinar, N., Kaplan, H. and Kleiman, M.: 1988, ‘Characterization of Concentration Fluctuations of a Surface Plume in a Neutral Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 45, 157–175.
Finnigan, J. J., Raupach, M. R., Bradley, E. F. and Aldis, G. K.: 1990, ‘A Wind Tunnel Study of Turbulent Flow Over a Two-Dimensional Ridge’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 277–317.
Gong, W. and Ibbetson, A.: 1989, ‘A Wind Tunnel Study of Turbulent Flow Over Model Hills’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 49, 113–148.
Gong, W.: 1991, ‘A Wind Tunnel Study of Turbulent Dispersion Over Two and Three Dimensional Gentle Hills From Upwind Point Sources in Neutral Flow’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 54, 211–230.
Hanna, S. R. and Insley, E. M.: 1989, ‘Time Series Analysis of Concentration and Wind Fluctuations’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 47, 131–147.
Hunt, J. C. R.: 1985, ‘Turbulent Diffusion From Sources in Complex Flows’,Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 17, 447–485.
Hunt, J. C. R. and Weber, A. H.: 1979, ‘A Lagrangian Statistical Analysis of Diffusion from a Ground Level Source in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’,Quart. J. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 105, 423–443.
Hunt, J. C. R.: 1980, ‘Wind Over Hills’,Dept. of Geosciences, Grant No R805595, N.C. State U.
Jackson, P. S. and Hunt, J. C. R.: 1975, ‘Turbulent Wind Flow Over a Low Hill’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 101, 929–955.
Mylne, K. R. and Mason, P. J.: 1991, ‘Concentration Fluctuation Measurements in a Dispersing Plume at a Range of up to 1000 m’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 177–206.
Sawford, B. L.: 1987, ‘Conditional Concentration Statistics for Surface Plumes in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 38, 209–223.
Seinfeld, J. H.: 1986, ‘Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Air Pollution’, John Wiley and Sons, pp. 499–584.
Walmsley, J. L., Taylor, P. A. and Keith, T.: 1986, ‘A Simple Model of Neutrally Stratified Boundary Layer Flow Over Complex Terrain With Surface Roughness Modulations’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 36, 157–186.
Walmsley, J. L., Taylor, P. A. and Salmon, J. R.: 1988, ‘Simple Guidelines for Estimating Wind Speed Variations Due to Small Scale Topographic Features — An Update’,Climatol. Bull. 23, 3–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crooks, G., Ramsay, S. A wind tunnel study of mean and fluctuating concentrations in a plume dispersing over a two-dimensional hill. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 66, 155–172 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705464
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705464