Conclusions
-
1.
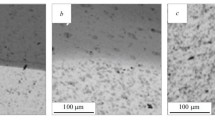
With increasing hydrogen concentrations there is no noticeable change in lattice constant c ofα titanium alloys, while the hardness and yield strength increase smoothly.
-
2.
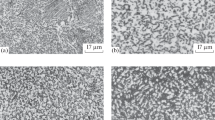
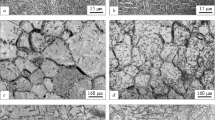
The relative elongation and reduction in section depend greatly on the grain size and the associated morphology of hydrides. Alloys of titanium with hydrogen having fine-grained hydrides have relativel high values of δ and ψ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
G. Lenning, C. Craighead, and R. Jaffee, Trans. AIME,200, 367.
W. Pearson, Handbook of Lattice Spacings and Structure of Alloys, Pergamon Press, London-New York (1958).
Additional information
Moscow Aviation Technology Institute. A. A. Baikov Institute of Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 12, pp. 57–58, December, 1978.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bukhanova, A.A., Egiz, I.V. Mechanical properties and lattice constant of Ti−Al−H alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 20, 1029–1031 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703286
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703286