Conclusions
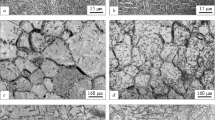
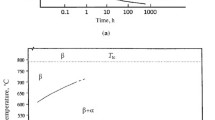
With prolonged low-temperature heating, alloys VT3-1 and VT9 tend to the stable condition corresponding to the heating temperature. This is accompanied by a change in the quantity of β phase and the concentration of β-stabilizing elements in β phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. I. Ermolova, "X-ray analysis of the quantity of β phase in titanium-base alloys," Zavod. Lab., No. 5, 577 (1965).
N. F. Lashko et al., Physicochemical Methods of Phase Analysis of Steels and Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1971).
M. I. Ermolova and O. P. Solonina, "X-ray investigation of phase transformations during heat treatment of titanium alloy VT3-1," Fiz. Metal. Metalloved.,23, No. 1, 63 (1967).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 42–46, May. 1977.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gus'kova, E.I., Ermolova, M.I., Lashko, N.F. et al. Effect of prolonged heating on the thermal stability of phases inα +β titanium alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 19, 381–384 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703013
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703013